Credit: Reidar Hahn/Fermilab
What do you get when you revive a beautiful 20-year-old physics machine, carefully transport it 3,200 miles over land and sea to its new home, and then use it to probe strange happenings in a magnetic field? Hopefully you get new insights into the elementary particles that make up everything.
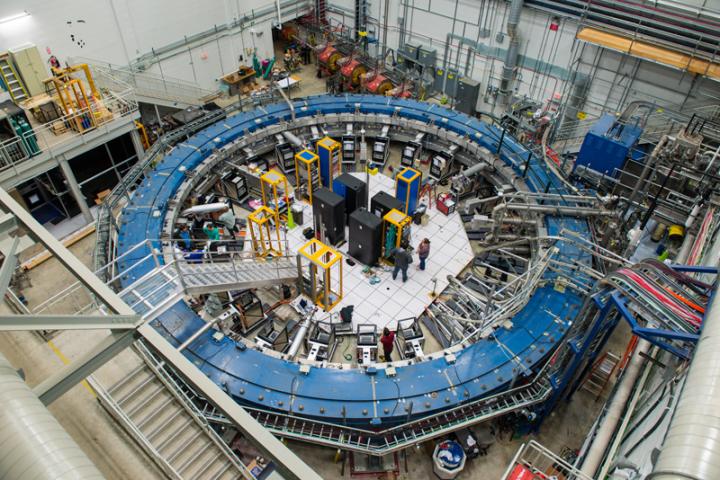
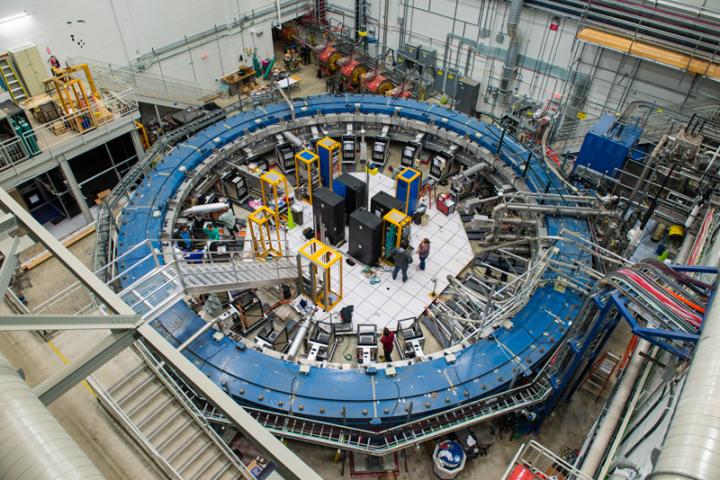
The Muon g-2 experiment, located at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, has begun its quest for those insights. On May 31, the 50-foot-wide superconducting electromagnet at the center of the experiment saw its first beam of muon particles from Fermilab's accelerators, kicking off a three-year effort to measure just what happens to those particles when placed in a stunningly precise magnetic field. The answer could rewrite scientists' picture of the universe and how it works.
"The Muon g-2 experiment's first beam truly signals the start of an important new research program at Fermilab, one that uses muon particles to look for rare and fascinating anomalies in nature," said Fermilab Director Nigel Lockyer. "After years of preparation, I'm excited to see this experiment begin its search in earnest."
Getting to this point was a long road for Muon g-2, both figuratively and literally. The first generation of this experiment took place at the U.S. DOE's Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York state in the late 1990s and early 2000s. The goal of the experiment was to precisely measure one property of the muon — the particles' precession, or wobble, in a magnetic field. The final results were surprising, hinting at the presence of previously unknown phantom particles or forces affecting the muon's properties.
The new experiment at Fermilab will make use of the laboratory's intense beam of muons to definitively answer the questions the Brookhaven experiment raised. And since it would have cost 10 times more to build a completely new machine at Brookhaven rather than move the magnet to Fermilab, the Muon g-2 team transported that large, fragile superconducting magnet in one piece from Long Island to the suburbs of Chicago in the summer of 2013.
The magnet took a barge south around Florida, up the Tennessee-Tombigbee waterway and the Illinois River, and was then driven on a specially designed truck over three nights to Fermilab. And thanks to a GPS-powered map online, it collected thousands of fans over its journey, making it one of the most well-known electromagnets in the world.
"Getting the magnet here was only half the battle," said Chris Polly, project manager of the Muon g-2 experiment. "Since it arrived, the team here at Fermilab has been working around the clock installing detectors, building a control room and, for the past year, adjusting the uniformity of the magnetic field, which must be precisely known to an unprecedented level to obtain any new physics. It's been a lot of work, but we're ready now to really get started."
That work has included the creation of a new beamline to deliver a pure beam of muons to the ring, the installation of a host of instrumentation to measure both the magnetic field and the muons as they circulate within it, and a year-long process of "shimming" the magnet, inserting tiny pieces of metal by hand to shape the magnetic field. The field created by the magnet is now three times more uniform than the one it created at Brookhaven.
Over the next few weeks the Muon g-2 team will test the equipment installed around the magnet, which will be storing and measuring muons for the first time in 16 years. Later this year, they will start taking science-quality data, and if their results confirm the anomaly first seen at Brookhaven, it will mean that the elegant picture of the universe that scientists have been working on for decades is incomplete and that new particles or forces may be out there, waiting to be discovered.
"It's an exciting time for the whole team, and for physics," said David Hertzog of the University of Washington, co-spokesperson of the Muon g-2 collaboration. "The magnet has been working, and working fantastically well. It won't be long until we have our first results and a better view through the window that the Brookhaven experiment opened for us."
###
The Muon g-2 collaboration includes more than 150 scientists and engineers from more than 30 institutions in nine countries.
The Muon g-2 experiment is supported by DOE's Office of Science and the National Science Foundation.
Fermilab is America's premier national laboratory for particle physics research. A U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science laboratory, Fermilab is located near Chicago, Illinois, and operated under contract by the Fermi Research Alliance LLC. Visit Fermilab's website at http://www.fnal.gov and follow us on Twitter @Fermilab.
The DOE Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit http://science.energy.gov.
Media Contact
Andre Salles
[email protected]
630-840-3351
@Fermilab
http://www.fnal.gov
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag