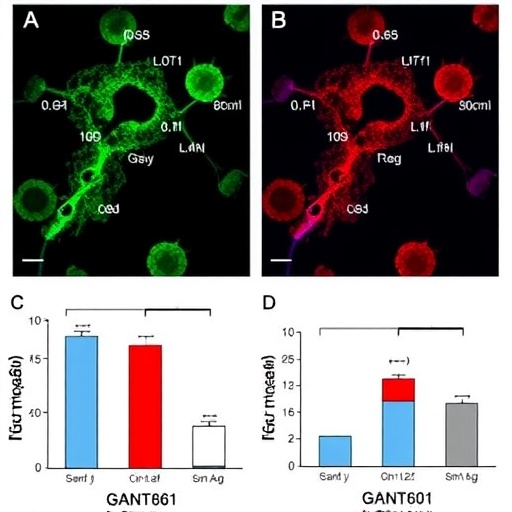
Recent advances in cancer research have unveiled promising therapeutic strategies, particularly in addressing complex malignancies such as anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). One of the most recent studies sheds light on the potential of GANT61, a small molecule inhibitor, in modulating vital signaling pathways to combat this aggressive form of lymphoma. The study has identified GANT61’s capacity to suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis in ALK-positive ALCL, marking a crucial step forward in therapeutic strategies for this challenging disease.
The hallmark feature of ALCL lies in its genetic profile, particularly the presence of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements. These alterations lead to the production of active oncogenic fusion proteins that drive unchecked cell growth and survival. GANT61 has emerged as a noteworthy compound, primarily due to its ability to inhibit the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in various cancer types, including ALCL. By targeting this pathway, researchers aim to disrupt the proliferative signals that contribute to tumor growth.
Through rigorous in vitro experiments, the research team led by Chen et al. demonstrated that GANT61 not only impairs cell growth but also promotes apoptosis in ALK-positive ALCL cells. The mechanism detailed in the study reveals that GANT61 targets the Hh-PIK3IP1-Akt signaling axis, effectively curtailing the proliferation signals that are often elevated in cancer cells. This mechanism underscores the multifaceted approach needed to tackle cellular signaling pathways that have long been implicated in oncogenesis.
Detailed analysis further uncovered that GANT61’s inhibition of the Hh pathway leads to a significant downregulation of downstream effectors crucial for survival and proliferation. Particularly, PIK3IP1, a pivotal regulator, appears to be directly influenced by GANT61 treatment, which ultimately results in decreased levels of activated Akt kinase. This cascade of molecular events highlights the intricate relationship between the Hh signaling pathway and PI3K/Akt signaling, both of which are integral to sustaining malignant growth.
Additionally, apoptosis was thoroughly assessed using various assays, including Annexin V staining and caspase activity measurements. These evaluations provided compelling evidence that GANT61 treatment notably enhances apoptotic cell death in ALK-positive ALCL models, thus illustrating its potential as a viable therapeutic agent. The ability to selectively induce apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing normal tissues stands at the forefront of developing targeted therapies that minimize collateral damage.
The implications of these findings are profound. With ALCL being notoriously difficult to treat, given its aggressive nature and tendency to relapse, identifying novel agents like GANT61 represents a beacon of hope for patients and clinicians alike. This study advocates for further investigation into GANT61’s clinical efficacy, emphasizing the necessity for clinical trials that could validate its therapeutic potential in humans.
Moreover, the research opens avenues for combination therapies as well, suggesting that GANT61 could be synergistically used with other treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy. By strategically integrating GANT61 into existing treatment regimens, we may achieve enhanced therapeutic outcomes, ultimately improving survival rates for ALCL patients.
The elucidation of the Hh-PIK3IP1-Akt signaling axis as a target for GANT61 not only reinforces the significance of this pathway in ALK-positive ALCL but also encourages the exploration of other inhibitors that act through similar mechanisms. It is vital to continue exploring the breadth of the Hedgehog signaling pathway’s involvement in various cancers as it could unveil additional vulnerabilities that can be targeted by innovative therapeutic strategies.
On a broader scale, this study exemplifies the shift towards precision medicine in oncology, where understanding specific molecular alterations can guide treatment selection. As researchers continue to decipher the complexities of tumor biology, the integration of advanced molecular strategies into therapy promises to reshape the landscape of cancer treatment fundamentally.
The search for effective treatment options for diseases like ALCL is an ongoing battle, one that demands continuous investment in research and development. The findings by Chen et al. reinforce the idea that innovative approaches, such as unraveling the signaling pathways that underlie cancer, can lead to breakthroughs that significantly affect patient outcomes. GANT61 stands as a potent reminder of the scientific community’s commitment to discovering viable solutions for even the most daunting challenges in cancer care.
Looking ahead, the implications of this research extend beyond ALCL. By leveraging the insights gained from the Hedgehog signaling pathway, research could impact other malignancies where similar pathways are aberrantly activated. This broader perspective highlights the potential for new therapeutic avenues that intertwine various dimensions of cancer biology, paving the way for more effective treatments across a spectrum of cancers.
In conclusion, the emergence of GANT61 as an influential player in the fight against ALCL underscores the remarkable progress being made in the realm of cancer therapeutics. The study not only reveals significant findings regarding its mechanisms of action but also instills hope for future breakthroughs in lymphoma treatment. As the scientific community continues to unlock the secrets of complex signaling networks, the prospects of more targeted and effective treatments become increasingly attainable.
Subject of Research: Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) and the effects of GANT61.
Article Title: GANT61 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in ALK-Positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma via modulating the Hh-PIK3IP1-Akt signaling axis.
Article References: Chen, H., Gao, J., Li, C. et al. GANT61 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in ALK-Positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma via modulating the Hh-PIK3IP1-Akt signaling axis. Ann Hematol 105, 54 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-026-06827-2
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-026-06827-2
Keywords: GANT61, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, Hedgehog signaling pathway, apoptosis, ALK-positive.
Tags: ALK-positive ALCL treatmentanaplastic large cell lymphoma therapyapoptosis induction in lymphomacancer research advancementsexperimental cancer therapeuticsGANT61 small molecule inhibitorHedgehog signaling pathway inhibitioninnovative approaches in lymphoma treatmentoncogenic fusion proteins in ALCLsignaling modulation in malignanciessuppressing tumor growth in ALCLtargeted cancer therapies