Credit: Tokyo Institute of Technology
In living organisms, free metal ions are stored and transported through proteins assembled into highly ordered structures such as protein cages via a reaction called biomineralization. This sophisticated biological strategy has attracted the attention of biotechnologists who speculate that natural ion-storage protein cages can be used to grow metal nanoparticles with desired properties.
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are known for their excellent functions in catalysis, bioimaging, drug delivery, and therapy; therefore, the synthesis of AuPs with controlled sizes and shapes is very important for their application in nanomedicine. In protein scaffolds, AuNPs are formed by a sequential process involving Au deposition and agglomeration into small nanoclusters which act as nucleation centers for AuNP growth. However, the dynamic mechanism underlying the formation of Au nanoclusters in protein environments remains unclear.
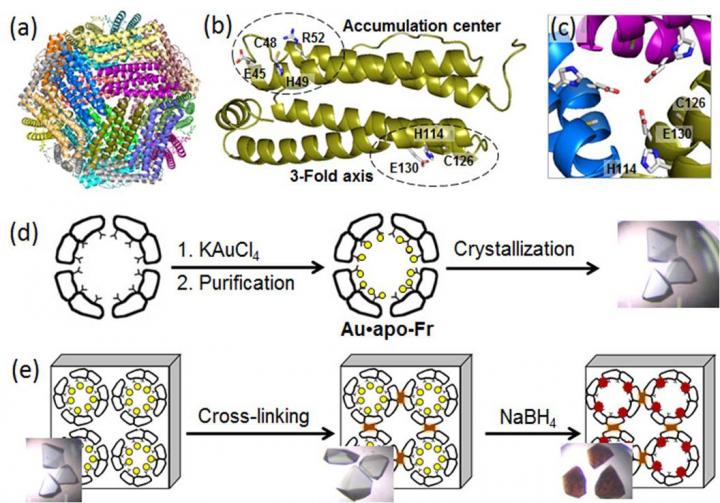
To disclose molecular processes behind AuNP growth in protein nanocages, a group of biomolecular engineers at Tokyo Institute of Technology, led by Takafumi Ueno, used high-resolution crystallography and analyzed the formation of Au nanoclusters in ferritin. A universal intracellular iron-storage protein produced by almost all living organisms, ferritin forms a self-assembled 24-subunit nanocage with two specific metal-binding sites: the 3-fold axis channel and the accumulation center (Figure). Since Au ions have high affinity for sulfur, the scientists modified the accumulation center by introducing an additional sulfur-containing cystein residue to enhance Au uptake into the protein cage. Then, they reinforced Au-containing ferritin crystals by cross-linking in glutaraldehyde (Figure) to maintain their lattice structure. These modifications enabled the reduction of Au ions in the crystals and determination of binding positions of Au ions inside the ferritin cage by high resolution crystallography.
In the next step, the immobilized Au ions were reduced into Au(0) atoms using a reducing agent (NaBH4). As a result, the scientists could observe that the reduced Au agglomerated into nanoclusters formed in the 3-fold symmetric channels and in the metal accumulation centers (Figure), which was due to the gradual Au movement and conformational changes of surrounding amino acids.
The results obtained by Professor Ueno and his colleagues uncover the mechanism behind the formation of Au nanoclusters which are expected as nucleation centers for subsequent AuNP growth in the unique protein environment, providing a platform for future investigation of biomineralization and nanoparticle synthesis in biomolecular scaffolds.
###
Media Contact
Emiko Kawaguchi
[email protected]
81-357-342-975
http://www.titech.ac.jp/english/index.html
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag