In polymers, the competition between the folding and aggregation of chains, both at an individual level and between chains, can determine the mechanical, thermal, and conductive properties of such materials. Understanding the interplay of folding and aggregation presents a significant opportunity for the development and discovery of polymeric materials with tailored properties and functionalities.
In polymers, the competition between the folding and aggregation of chains, both at an individual level and between chains, can determine the mechanical, thermal, and conductive properties of such materials. Understanding the interplay of folding and aggregation presents a significant opportunity for the development and discovery of polymeric materials with tailored properties and functionalities.
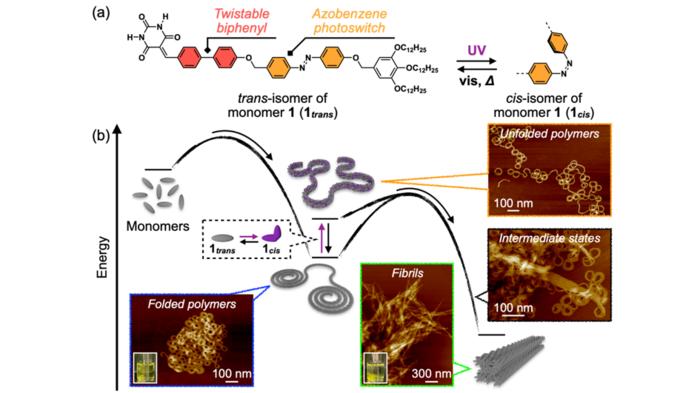
This also holds true for non-covalent counterparts of conventional covalent polymers, i.e., supramolecular polymers (SPs). SPs are expected to have practical applications as novel stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Most SPs have a monotonous one-dimensional linear structure that tends to cause interchain aggregation, but there are very few reports of SPs that can form various higher-order structures through main chain folding. The development of an SP that exhibits both intrachain folding and interchain aggregation would provide a new guideline for creating novel SP materials whose properties can be controlled by higher-order structures.
A recent study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 25, 2024, reported a new folded SP that spontaneously undergoes interchain aggregation and converts into crystalline aggregates. With the help of atomic force microscopy (AFM), the research team has demonstrated the relationship between unfolding and aggregation. The study was led by Professor Shiki Yagai from Chiba University, with Kenta Tamaki, a doctoral course student at the Graduate School of Science and Engineering at Chiba University, as the first author.
“Originally, we found a monomer structure that polymerized in a spiral shape. This time, we partially changed the structure of the unit that drives the polymerization of the monomer to investigate the monomer-polymer relationship. To our surprise, we observed a phenomenon where the spiral spontaneously unfolds, and the different chains bundle together. We then incorporated a photo-switchable molecule so that this ‘spontaneous’ phenomenon could occur at ‘arbitrary timing’ through light, which provides the background for our research,“ says Prof. Yagai, speaking of the inspiration behind this study.
To design the new system, the team opted for twistable biphenyl and photoresponsive azobenzene units as a core, which self-assembled into the desired SPs. The SPs initially formed in a folded state slowly underwent rearrangement in internal molecular order over half a day and aggregated to a crystalline state. The inclusion of azobenzene units in the SPs led to photoinduced unfolding, which significantly accelerated the process by loosening the intrachain stabilization between folded loops.
The researchers observed that when the folded SP solution was left to stand at 20oC for several days, the polymers spontaneously underwent structural transition and precipitated. When the precipitate was visualized using AFM, they observed a unique intermediate state that appeared to be a coalescence of curved chains en route to the unified straight fibril structures. This intriguing image reminded the researchers of the interchain aggregation often observed in biological systems when proteins misfold, leading to amyloid fibril formation.
Furthermore, the team revealed the reason behind this structural transformation. This included intrachain molecular ordering due to conformational changes in the biphenyl unit and interchain ordering from the alignment of the aliphatic tails covering the exterior of the main chains. This mechanism is similar to the crystallization of conventional covalent polymers. The team corroborated this mechanism using the photoisomerization of the azobenzene unit. When they irradiated UV light to the folded SP solution to induce conformational changes in the azobenzene units, the unfolding of the main chain immediately occurred, and interchain aggregation was significantly accelerated.
Overall, this study opens unforeseen perspectives on the folding and aggregation phenomenon. The mesoscale SPs formed via self-assembly of a large number of molecules can serve as a useful model system to examine the dynamics between individual main chains at a molecular level. This, in turn, opens up new avenues for innovation in trans-scale materials science.
“These phenomena have traditionally been investigated using spectroscopic or macroscopic observations, reflecting the averaged behavior of the whole system. Therefore, the construction of more observable mesoscale models is expected to contribute significantly to the advancement of materials science. We are hopeful that these insights can encourage the development of meso-scale molecular assemblies with meaningful higher-order structures,” concluded Prof. Yagai.
About Professor Shiki Yagai from Chiba University
Shiki Yagai is a Professor at the Division of Advanced Science and Engineering, Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan. In 2002, he received his Ph.D. from Ritsumeikan University, Japan. He joined Chiba University as an Assistant Professor and was promoted to Full Professor in 2017. He has over 160 publications in the fields of organic chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, and nanotechnology, with more than 7,500 citations. He has been bestowed with several awards, the most recent being the Swiss Chemical Society Lectureships (2017). Currently, Prof. Yagai and his team are working on the development of supramolecular functional materials.
Journal
Journal of the American Chemical Society
DOI
10.1021/jacs.4c07878
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Photoresponsive Supramolecular Polymers Capable of Intrachain Folding and Interchain Aggregation
Article Publication Date
25-Jul-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.