Microplastics pose a great threat to human health. These tiny plastic debris can enter our bodies through the water we drink and increase the risk of illnesses. They are also an environmental hazard; found even in remote areas like polar ice caps and deep ocean trenches, they endanger aquatic and terrestrial lifeforms.
Credit: Soumi Dutta
Microplastics pose a great threat to human health. These tiny plastic debris can enter our bodies through the water we drink and increase the risk of illnesses. They are also an environmental hazard; found even in remote areas like polar ice caps and deep ocean trenches, they endanger aquatic and terrestrial lifeforms.
To combat this emerging pollutant, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have designed a sustainable hydrogel to remove microplastics from water. The material has a unique intertwined polymer network that can bind the contaminants and degrade them using UV light irradiation.
Scientists have previously tried using filtering membranes to remove microplastics. However, the membranes can become clogged with these tiny particles, rendering them unsustainable. Instead, the IISc team led by Suryasarathi Bose, Professor at the Department of Materials Engineering, decided to turn to 3D hydrogels.
The novel hydrogel developed by the team consists of three different polymer layers – chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol and polyaniline – intertwined together, making an Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN) architecture. The team infused this matrix with nanoclusters of a material called copper substitute polyoxometalate (Cu-POM). These nanoclusters are catalysts that can use UV light to degrade the microplastics. The combination of the polymers and nanoclusters resulted in a strong hydrogel with the ability to adsorb and degrade large amounts of microplastics.
Most microplastics are a product of incomplete breakdown of household plastics and fibres. To mimic this in the lab, the team crushed food container lids and other daily-use plastic products to create two of the most common microplastics existing in nature: polyvinyl chloride and polypropylene.
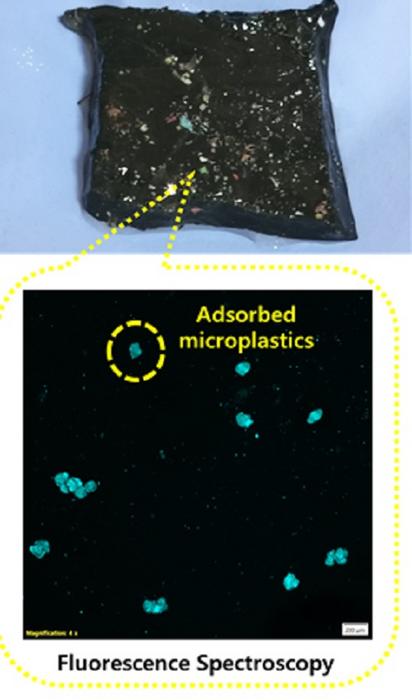
“Along with treatment or removal of microplastics, another major problem is detection. Because these are very small particles, you cannot see them with the naked eye,” explains Soumi Dutta, first author of the study published in Nanoscale, and SERB National Post-doctoral fellow at the Department of Materials Engineering.
To solve this problem, the researchers added a fluorescent dye to the microplastics to track how much was being adsorbed and degraded by the hydrogel under different conditions. “We checked the removal of microplastics at different pH levels of water, different temperatures, and different concentrations of microplastics,” explains Dutta.
The hydrogel was found to be highly efficient – it could remove about 95% and 93% of the two different types of microplastics in water at near-neutral pH (∼6.5). The team also carried out several experiments to test how durable and strong the material was. They found that the combination of the three polymers made it stable under various temperatures.
“We wanted to make a material that is more sustainable and can be used repetitively,” explains Bose. The hydrogel could last for up to five cycles of microplastic removal without significant loss of efficacy. What’s more, Bose points out, is that once it has outlived its use, the hydrogel can be repurposed into carbon nanomaterials that can remove heavy metals like hexavalent chromium from polluted water.
Moving forward, the researchers plan to work with collaborators to develop a device that can be deployed on a large scale to help clean up microplastics from various water sources.
Journal
Nanoscale
DOI
10.1039/D3NR06115A
Article Title
Polyoxometalate nanocluster-infused triple IPN hydrogels for excellent microplastic removal from contaminated water: detection, photodegradation, and upcycling
Article Publication Date
5-Feb-2024




