Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women, posing a serious threat to the female health. Due to the high inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity of breast cancer, clinical treatment and prognosis can vary greatly in patients. Currently, chemotherapy is the main systemic treatment for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), a common type of breast cancer that does not have any of the receptors that are commonly found in breast cancer. However, treatment with the a uniform high-dose chemotherapy regimen without molecular subtyping frequently yields suboptimal efficacy, adding further burden and discomfort to patients.
Credit: Li S. M., Bi X., Yang F., et al.,
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women, posing a serious threat to the female health. Due to the high inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity of breast cancer, clinical treatment and prognosis can vary greatly in patients. Currently, chemotherapy is the main systemic treatment for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), a common type of breast cancer that does not have any of the receptors that are commonly found in breast cancer. However, treatment with the a uniform high-dose chemotherapy regimen without molecular subtyping frequently yields suboptimal efficacy, adding further burden and discomfort to patients.
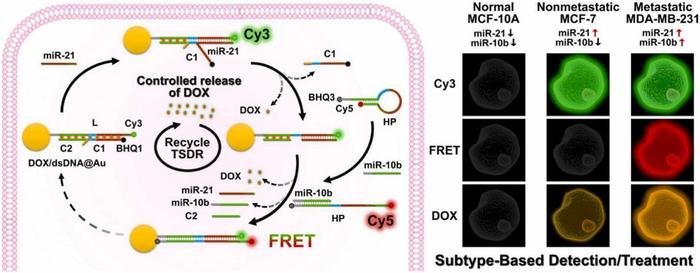
In a study published in the KeAi journal Biomedical Analysis, a group of researchers from China outline a new discrimination and treatment approach — a dual-miRNA triggered DNA-programmed nanomachine capable of imaging endogenous miRNA expressions. This approach makes subtype-based detection possible, thereby regulating drug release for chemotherapy.
“For the diagnosis and subtyping of breast cancer, histological examination of puncture biopsy sample is the “gold standard”, but it is invasive and difficult to realize dynamic monitoring of tumor progression and prognosis for treatment guidance,” explains study’s corresponding author Yun Xiang, a professor in luminescence analysis and molecular sensing at Southwest University. “Fluorescence imaging techniques are capable of visualizing and monitoring minimal molecular changes occurring at early stage of cancers with high resolution and sensitivity. However, single miRNA imaging is not suitable for discrimination of cancel cell types.”
Notably, while previous studies have demonstrated that dual miRNA-triggered drug release can be applied for cancer therapy via the toehold-mediated strand displacement reactions (TSDR), tailored treatments such as high-dose chemotherapy in TNBC and conventional-dose chemotherapy in other breast subtypes, have not been realized.
“We developed a DNA-programmed nanomachine for effective discrimination and tailored treatment of specific breast cancer cell types,” says Shunmei Li, first author of the study. “It is a responsive therapy strategy towards to the various cell states. This intelligent nanomachine with controlled release of anti-cancer drug in specific cancer cell subtypes can reduce the side effect to normal cells and facilitate the targeted therapy, which is promising as a theranostics nanoplatform in precise medicine.”
###
Contact the author: Yun Xiang, Key Laboratory of Luminescence Analysis and Molecular Sensing, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, PR China. [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Biomedical Analysis
DOI
10.1016/j.bioana.2024.01.001
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Dual-microRNA triggered and DNA-programmed nanomachine for subtype-based detection and tailored treatment of breast cancer cells
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.