Science China Life Sciences recently reported on the research results of Lanjuan Li’s team from Zhejiang university. Recent advances in microbiome research have revealed complex changes in gut microecology across various disease states, highlighting their profound impact on disease progression. While numerous studies have emphasized the crucial roles of microbiota and their metabolites in disease advancement, understanding the dynamics of gut fungal variations during the progression of nonviral liver diseases in both humans and rodent models has remained elusive. This knowledge gap underscores the urgent need for further exploration of the potential of fungal biomarkers and therapeutic targets for liver diseases.
Credit: ©Science China Press
Science China Life Sciences recently reported on the research results of Lanjuan Li’s team from Zhejiang university. Recent advances in microbiome research have revealed complex changes in gut microecology across various disease states, highlighting their profound impact on disease progression. While numerous studies have emphasized the crucial roles of microbiota and their metabolites in disease advancement, understanding the dynamics of gut fungal variations during the progression of nonviral liver diseases in both humans and rodent models has remained elusive. This knowledge gap underscores the urgent need for further exploration of the potential of fungal biomarkers and therapeutic targets for liver diseases.
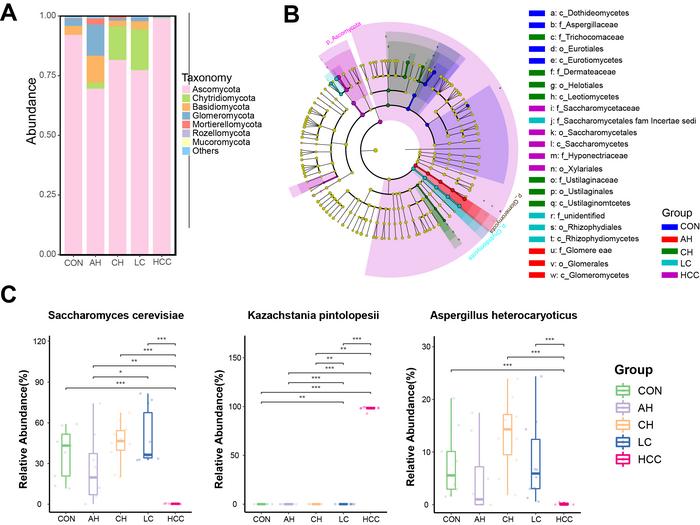
Lanjuan Li’s team, using mouse models of DEN-induced and CCl4-promoted hepatocarcinogenesis, found that during liver disease progression, the abundance of Chytridiomycota increased initially, but was later replaced by Ascomycota in HCC. Notably, Kazachstania pintolopesii predominated in the HCC group, while Saccharomyces cerevisiae significantly decreased (Figure 1).
The team collected fecal samples from clinical liver disease patients for validation. They found consistency with mouse models, showing disrupted Ascomycota in HCC, and higher Candida genus abundance in the HCC group compared to the LC group (Figure 2).
This study also conducts additional investigations that assessed the impact of C. albicans and S. cerevisiae on LC-HCC progression. Administration of these fungi revealed effects on tumor diameter and liver disease progression in mice, with outcomes ranging from aggravation to amelioration. This indicates that gut mycobiota may function not only as biomarkers for the progression of liver diseases but also as promising avenues for prevention or therapeutic interventions (Figure 3).
Journal
Science China Life Sciences
DOI
10.1007/s11427-023-2458-1




