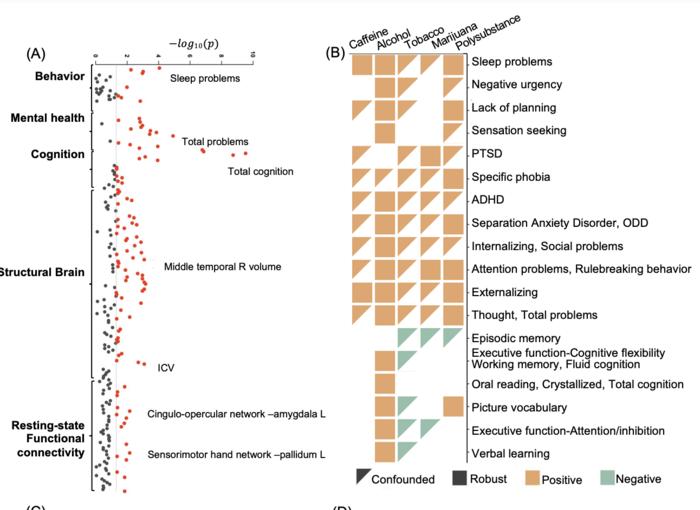
An observational study found links between prenatal substance exposure and mental health in children 10–12, but also found that controlling for environment and genetics eliminated many associations. Qiang Luo and colleagues analyzed longitudinal data from almost 10,000 participants in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development cohort, looking for associations of maternal self-report of prenatal exposure to caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana with mental health outcomes from age 10 to 12. Although the authors found many associations between prenatal exposure to the substances studied and neurobehavioral problems, many of these associations diminished when the authors controlled for environment and genetics. Environmental risk factors were captured using metrics such as planned birth, vitamin intake during pregnancy, duration of breastfeeding, premature birth, parental ages at birth, parental partnership, parental education level, family income, and measures of neighborhood safety. Genetic context was established by family history of psychiatric disorders and polygenic risk scores. None of the associations between prenatal exposure to cigarette smoke and outcomes at age 10–12 remained significant after genetics and environment were considered. On the other hand, prenatal exposure to alcohol remained significantly correlated to sleep problems and mental health problems at age 10–12 even after controlling for environment and genetics. In addition, the authors found that contrary to earlier reports of prenatal alcohol exposure correlating with smaller cerebral gray matter volumes in later life, children who has been exposed to alcohol in utero had larger gray matter volumes. According to the authors, the increased gray matter volume, accompanied by low functioning of other brain regions, may reflect a compensatory response of some brain regions coping with the impact of maternal alcohol use.
Credit: Gu et al.
An observational study found links between prenatal substance exposure and mental health in children 10–12, but also found that controlling for environment and genetics eliminated many associations. Qiang Luo and colleagues analyzed longitudinal data from almost 10,000 participants in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development cohort, looking for associations of maternal self-report of prenatal exposure to caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana with mental health outcomes from age 10 to 12. Although the authors found many associations between prenatal exposure to the substances studied and neurobehavioral problems, many of these associations diminished when the authors controlled for environment and genetics. Environmental risk factors were captured using metrics such as planned birth, vitamin intake during pregnancy, duration of breastfeeding, premature birth, parental ages at birth, parental partnership, parental education level, family income, and measures of neighborhood safety. Genetic context was established by family history of psychiatric disorders and polygenic risk scores. None of the associations between prenatal exposure to cigarette smoke and outcomes at age 10–12 remained significant after genetics and environment were considered. On the other hand, prenatal exposure to alcohol remained significantly correlated to sleep problems and mental health problems at age 10–12 even after controlling for environment and genetics. In addition, the authors found that contrary to earlier reports of prenatal alcohol exposure correlating with smaller cerebral gray matter volumes in later life, children who has been exposed to alcohol in utero had larger gray matter volumes. According to the authors, the increased gray matter volume, accompanied by low functioning of other brain regions, may reflect a compensatory response of some brain regions coping with the impact of maternal alcohol use.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
Prenatal substance exposure and child health: Understanding the role of environmental factors, genetics, and brain development
Article Publication Date
30-Jan-2024




