A centuries-old technique for constructing arched stone windows has inspired a new way to form tailored nanoscale windows in porous functional materials called metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Credit: © 2023 KAUST.
A centuries-old technique for constructing arched stone windows has inspired a new way to form tailored nanoscale windows in porous functional materials called metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
The method uses a molecular version of an architectural arch-forming “centring formwork“ template to direct the formation of MOFs with pore windows of predetermined shape and size.[1]. New MOFs designed and made in this way range from narrow-windowed materials with gas separation potential to larger-windowed structures with potential medical applications due to their excellent oxygen-adsorption capacity.
“One of the most challenging goals in new structure design is the precise control of structure formation,” says Aleksandr Sapianik, a postdoc in the group of Mohamed Eddaoudi, who led the research. For reticular chemistry — the assembly of molecular building blocks into porous crystalline materials such as MOFs — the centering formwork concept might offer that precise control, the team realized.
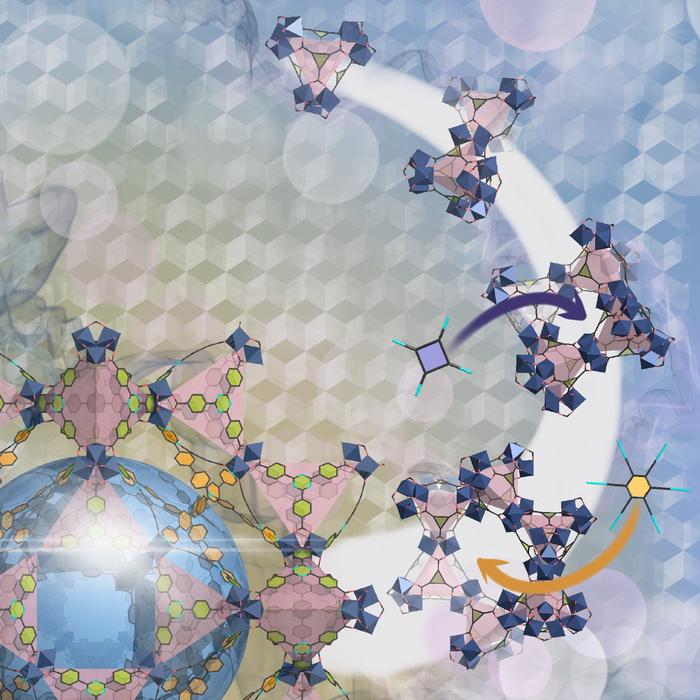
The starting point of the research was a zeolite-like MOF (ZMOF), which usually features pentagonal windows framed by building blocks called supertetrahedra (ST). “Our goal was to control ST arrangement to change from this well-known topology to one not reported before with these building blocks,” Sapianik says.
The team developed centring structure-directing agents (cSDA) to control ST alignment and form ZMOF windows of new shapes and sizes. One set of cSDAs, designed to tighten the angle between adjoining ST units, created small windows. Another set, designed to expand the angle between ST units, gave larger windows.
“MOF pore size and volume are important parameters that affect their application,” says Marina Barsukova, a postdoc in Eddaoudi’s team. One large-windowed ZMOF the team designed, Fe-sod-ZMOF-320, showed the highest oxygen adsorption capacity of any MOF known. “This property is important in the medical and aerospace industries, where the high capacity would increase oxygen storage in a cylinder, or enable smaller cylinders for easier transport,” Barsukova says. The same ZMOFs also performed well for storage of methane and hydrogen, which are potential fuels. Other ZMOFs in the family with narrow windows showed potential for gas separation of molecular mixtures.
The cSDA concept offers multiple benefits enhancing MOF performance, says Vincent Guillerm, a research scientist in Eddaoudi’s group. “The cSDA partitions big windows into smaller ones, which our preliminary results suggest will be useful for chemical separations,” he says. “It also offers additional internal pore surface, which can help to improve gas storage, and reinforces the MOF framework, which should improve the material’s stability,” he adds.
“The centring approach we have developed is another powerful strategy in the repertoire of reticular chemistry, offering great potential for made-to-order MOFs for applications in energy security and environmental sustainability,” Eddaoudi says.
Journal
Nature Synthesis
DOI
10.1038/s44160-023-00401-8
Article Title
Face-directed assembly of tailored isoreticular MOFs using centring structure-directing agents
Article Publication Date
2-Oct-2023




