Precise control of light is a crucial requirement in optical imaging, sensing, and communication. Traditional lenses employed for the purpose have limitations, necessitating more precise and compact solutions. To address this need, researchers have developed metalenses, ultrathin lenses constructed from nanomaterials that are smaller in size than the wavelength of light. These sub-wavelength elements provide the means to manipulate light waves with exceptional precision, facilitating a precise control of the amplitude, phase, polarization, and direction of light waves.
Credit: Tian et al., doi 10.1117/1.APN.2.5.056002
Precise control of light is a crucial requirement in optical imaging, sensing, and communication. Traditional lenses employed for the purpose have limitations, necessitating more precise and compact solutions. To address this need, researchers have developed metalenses, ultrathin lenses constructed from nanomaterials that are smaller in size than the wavelength of light. These sub-wavelength elements provide the means to manipulate light waves with exceptional precision, facilitating a precise control of the amplitude, phase, polarization, and direction of light waves.
Moreover, compared to bulky lenses, metalenses are easier to produce and are ideal for miniaturized and highly integrated optical devices. However, the sub-wavelength elements also make them susceptible to chromatic aberration. This is a condition where when light passes through a metalens, each wavelength undergoes a different phase shift upon interaction with the sub-wavelength structures. As a result, the various colors or wavelengths of light do not converge at the same point, leading to a loss of focus and reduced image quality.
Now, in a new study published in Advanced Photonics Nexus, researchers have presented a novel approach for creating broadband achromatic and polarization-insensitive metalenses (BAPIML). Their approach leverages the Rayleigh criterion for spot resolution, a fundamental principle in optics used to define the minimum resolvable detail in an imaging system. “The scientific and technical advances reported are notable as they offer a path towards resolving chromatic aberration in metasurfaces, a challenge that has hindered progress in the field,” points out journal editor Professor Alex Krasnok from Florida International University.
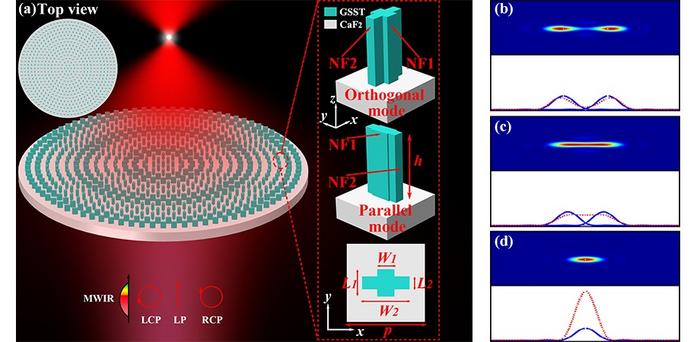
According to the Rayleigh criterion for spot resolution, closely spaced point sources can be resolved when the center of the diffraction pattern produced by one point source falls on the first minimum of the diffraction pattern of another point source. When the diffraction patterns approach this limit, the two points become indistinguishable from each other. This principle has been instrumental in designing telescopes and microscopes to distinguish celestial objects and capture the minutest details in tiny specimens, respectively. In this study, the researchers ingeniously applied this concept to develop instead two complementary metalenses that merge the bright spots into a single, focused spot.
They fabricated the two metalenses using nanofins made of a phase change material, Ge2Sb2Se4Te1. These nanofins were arranged in orthogonal or parallel orientations with respect to each other and designed to introduce a phase shift in the light passing through them. One of the nanofins acted as a half-wave plate for a wavelength of 4 µm, while the other served as a half-wave plate for a wavelength of 5 µm.
The metalenses, when illuminated by light, produce two distinct bright spots focused on different positions. However, by carefully adjusting the parameters, such as the radius and focal length of the metalenses, the researchers managed to merge the bright spots into a single focusing spot with an efficiency of up to 43 percent. Simply put, the lenses counteracted chromatic aberrations by focusing light of different wavelengths at the same point.
Finally, the researchers demonstrate the versatility of their approach by generating a broadband achromatic and polarization-insensitive focusing optical vortex. “Put simply, this work signifies that we are on the path towards creating lenses that can better handle light without distortion, and can potentially improve a variety of optical applications,” says Prof. Krasnok.
This new method for developing BAPIML opens doors to a wide range of improved imaging and optical applications, including molecular sensing, bioimaging, detectors, and holographic displays.
Read the Gold Open Access article by Tian et al., “Differentiated design strategies toward broadband achromatic and polarization-insensitive metalenses,” Adv. Photon. Nexus 2(5) 056002 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.APN.2.5.056002.
Journal
Advanced Photonics Nexus
DOI
10.1117/1.APN.2.5.056002
Article Title
Differentiated design strategies toward broadband achromatic and polarization-insensitive metalenses
Article Publication Date
22-Jul-2023




