The neurons in our bodies are dotted with tiny pores that let essential molecules pass in and out of our cells. Neurons need these channels to send the signals that allow us to move, think, and perceive the world around us. Now, structural biologists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have captured never-before-seen images of one of the largest pores in human neurons. It’s called calcium homeostasis modulator protein 1, or CALHM1 for short.
Credit: Furkawa lab/Cryo-EM Facility/Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
The neurons in our bodies are dotted with tiny pores that let essential molecules pass in and out of our cells. Neurons need these channels to send the signals that allow us to move, think, and perceive the world around us. Now, structural biologists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have captured never-before-seen images of one of the largest pores in human neurons. It’s called calcium homeostasis modulator protein 1, or CALHM1 for short.
Previous studies have shown that mutations in the Cahlm1 gene may be a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. CSHL’s new research reveals, for the first time, how the channel works in humans and how it can get jammed up.
CSHL Professor Hiro Furukawa and postdoc Johanna Syrjänen have been studying CALHM1 for several years. It seems to be involved in a vast array of physiological processes. In our tongues, CALHM1 detects tastes like sweet, sour, or umami. In our brains, CALHM1 may play a role in controlling the buildup of a plaque-forming protein associated with Alzheimer’s.
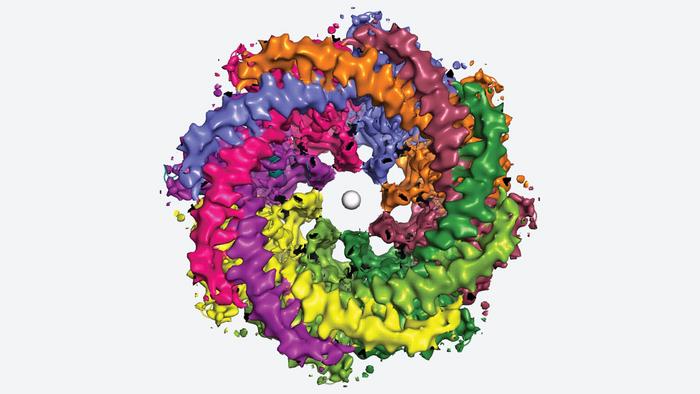
Furukawa, Syrjänen, and colleagues used a method called cryo-electron microscopy to generate detailed, three-dimensional images of the human CALHM1 channel. The images show how eight copies of the CALHM1 protein assemble together to form the circular channel. Each protein has a flexible arm that reaches into the pore, possibly controlling how it opens and closes. Syrjänen likens the arms to “octopus tentacles.”
The team also discovered that fatty molecules called phospholipids are critical for stabilizing and regulating the eight-part channel. Eggs, cereal, lean meats, and seafood all contain loads of these important fats. Additionally, Furukawa’s lab showed how a chemical that researchers use to block CALHM1 becomes lodged in the channel. That knowledge could be useful if someday researchers aim to develop a drug that targets CALHM1. Syrjänen says:
“If you are thinking way down the line, ‘Can we control taste perception or influence this protein?’ we now know one of the places where you could block the protein activity.”
Syrjänen notes that the human CALHM1 channel looks a lot like the version she and Furukawa studied in chickens in 2020. Determining the structure of the human protein proved more technically challenging. But, researchers agree, it’s vital for learning about the channel’s role in human health.
“There are numerous unanswered questions surrounding CALHM1,” Furukawa says. For example, how does the energy-carrying molecule, ATP, escape from cells via this channel? And could this trigger the body’s inflammatory response? “Our research group will continue unraveling this vital molecular machine to better understand the CALHM1 channel’s functionality.”
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-023-39388-3
Article Title
Structure of human CALHM1 reveals key locations for channel regulation and blockade by ruthenium red
Article Publication Date
28-Jun-2023




