Being obese significantly increases the chances of also developing mental disorders. This applies to all age groups, with women at higher risk than men for most diseases, as a recent study of the Complexity Science Hub and the Medical University of Vienna shows. The results were published in the specialist journal “Translational Psychiatry”.
Credit: © Complexity Science Hub
Being obese significantly increases the chances of also developing mental disorders. This applies to all age groups, with women at higher risk than men for most diseases, as a recent study of the Complexity Science Hub and the Medical University of Vienna shows. The results were published in the specialist journal “Translational Psychiatry”.
“We analyzed a population-wide national registry of inpatient hospitalizations in Austria from 1997 to 2014 in order to determine the relative risks of comorbidities in obesity and identify statistically significant sex differences,” explains Elma Dervic of the Complexity Science Hub. Consequently, it became evident that an obesity diagnosis significantly enhances the likelihood of a wide range of mental disorders across all age groups – including depression, nicotine addiction, psychosis, anxiety, eating and personality disorders. “From a clinical point of view, these results emphasise the need to raise awareness of psychiatric diagnoses in obese patients and, if necessary, to consult specialists at an early stage of diagnosis”, says Michael Leutner of the Medical University of Vienna.
FIRST DIAGNOSIS: OBESITY
“In order to find out which illness typically appeared prior and subsequently to the obesity diagnosis, we had to develop a new method,” explains Dervic. This allowed the researchers to determine if there were trends and typical patterns in disease occurrence.
In case of all co-diagnoses, with the exception of the psychosis spectrum, obesity was in all likelihood the first diagnosis made prior to the manifestation of a psychiatric diagnosis. “Until now, physicians often considered psychopharmacological medications to cause the association between mental disorders and obesity as well as diabetes. This may be true for schizophrenia, where we see the opposite time order, but our data does not support this for depression or other psychiatric diagnoses,” explains Alexander Kautzky from Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy of the Medical University Vienna. However, whether obesity directly affects mental health or whether early stages of psychiatric disorders are inadequately recognised is not yet known.
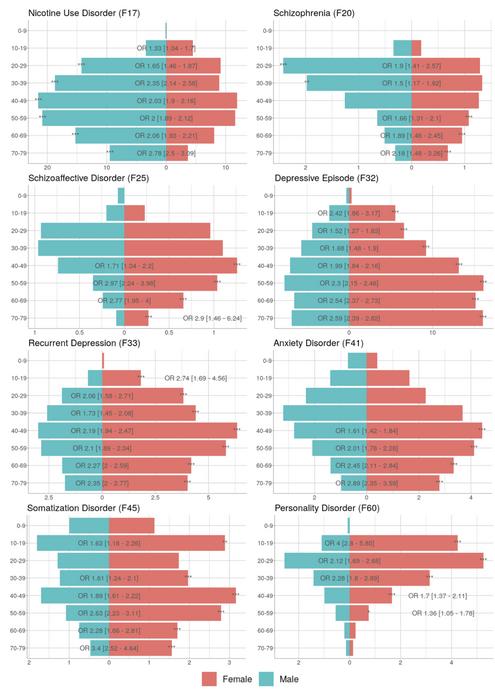
GREATER IMPACT IN WOMEN
Surprisingly, the researchers found significant gender differences for most disorders – with women showing an increased risk for all disorders except schizophrenia and nicotine addiction.
While 16.66% of obese men also suffer from nicotine abuse disorder, this is only the case in up to 8.58% of obese women. The opposite is true for depression. The rate of diagnosed depressive episodes was almost three times higher in obese women (13.3% obese; 4.8% non-obese). Obese men were twice as likely to be affected (6.61% obese; 3.21% non-obese).
COUNTERACT AT A YOUNG AGE
At present, obesity is a highly prevalent disease worldwide and affects more than 670 million people. The fact that the disease promotes metabolic disorders and serious cardio-metabolic complications (diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, and dyslipidaemia) has already been extensively researched.
Since this study now also shows that obesity often precedes severe mental disorders, the findings underscore its importance as a pleiotropic risk factor for health problems of all kinds. This is primarily true for young age groups, where the risk is most pronounced. For this reason, thorough screening for mental health problems in obese patients is urgently needed to facilitate prevention or ensure that appropriate treatment can be given, so the researchers conclude.
FIND OUT MORE
The study “Obesity as pleiotropic risk state for metabolic and mental health throughout life” has been published in Translational Psychiatry.
ABOUT THE COMPLEXITY SCIENCE HUB
The mission of the Complexity Science Hub (CSH Vienna) is to host, educate, and inspire complex systems scientists dedicated to making sense of Big Data to boost science and society. Scientists at the Complexity Science Hub develop methods for the scientific, quantitative, and predictive understanding of complex systems.
The CSH Vienna is a joint initiative of AIT Austrian Institute of Technology, Central European University CEU, Danube University Krems, Graz University of Technology, Medical University of Vienna, TU Wien, VetMedUni Vienna, Vienna University of Economics and Business, and Austrian Economic Chambers (WKO). https://www.csh.ac.at
ABOUT THE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA
The Medical University of Vienna (in short: MedUni Vienna) is one of the most traditional medical education and research facilities in Europe. With around 8,000 students, it is currently the largest medical training centre in the German-speaking world. With 6,000 employees, 30 departments and two clinical institutes, 13 medical theory centres and numerous highly specialised laboratories, it is one of Europe’s leading research establishments in the biomedical sector. MedUni Vienna also has a medical history museum, the Josephinum.
Journal
Translational Psychiatry
DOI
10.1038/s41398-023-02447-w
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Obesity as pleiotropic risk state for metabolic and mental health throughout life
Article Publication Date
30-May-2023




