Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that, when a stroke therapy is linked to a specific kind of lipid and injected into the blood, it is taken up preferentially in the stroke-lesioned brain
Credit: Department of Neurology and Neurological Science, TMDU
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that, when a stroke therapy is linked to a specific kind of lipid and injected into the blood, it is taken up preferentially in the stroke-lesioned brain
Tokyo, Japan – To get therapies into the brain after a stroke, researchers are increasingly making use of the blood–brain barrier, which allows only certain molecules to pass from the blood into the brain. In a study published earlier this year in Molecular Therapy, Japanese researchers have found that antisense oligonucleotides—specialized molecules that can modulate RNA and alter protein production—are preferentially taken up from the blood into areas of stroke damage when they’re linked to a specific kind of lipid known as α-tocopherol (TOC).
Current stroke therapies are only effective if they are delivered within a short window of time, which limits their effectiveness in many patients. Many new therapies are being investigated that can be applied outside this short window of opportunity. One such therapy involves the use of antisense oligonucleotides, which can be targeted to increase the production of beneficial proteins after a stroke, for example, or to decrease the production of harmful proteins. However, getting these molecules into the right area at the right time can be difficult, something that the researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University wanted to address.
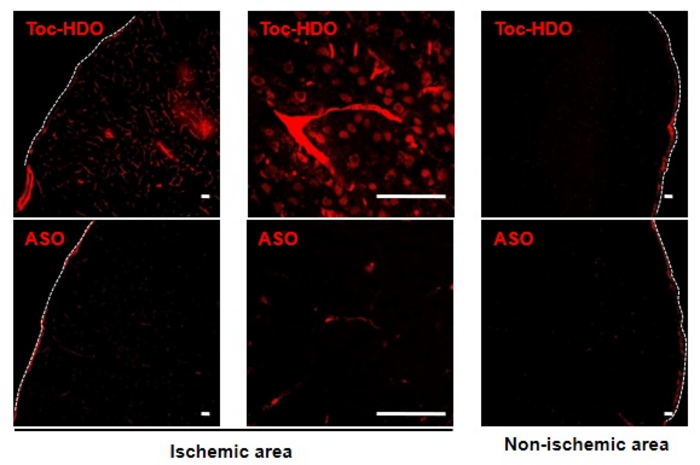
“We’ve recently developed an antisense oligonucleotide known as a DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide, or HDO,” says senior author of the study Takanori Yokota. “To see how different lipids affect the uptake of HDO in the brain, we linked it to either cholesterol or TOC and then injected it into the blood of mice who had been given an experimentally induced stroke in just one side of the brain.”
Unexpectedly, the TOC-linked molecules were observed at very high levels in the stroke-lesioned side of the brain only, whereas the cholesterol-linked molecules were high in both sides of the brain. This suggests that TOC specifically increases HDO uptake after stroke, while cholesterol does not. Furthermore, because HDO can be tailored to target different genes, it was used to silence a gene known to be beneficial in stroke. As expected, the researchers observed greater areas of stroke-related damage in the mice treated with this TOC-linked HDO.
“Together, our findings suggest that TOC-linked HDO is safe to use and is preferentially taken up and incorporated into cells in areas of stroke damage,” says Yokota. “This delivery method is potentially very useful for the targeted up- or down-regulation of protein expression after stroke.”
Given the relative lack of stroke therapies targeting the pathological processes that happen after a stroke, the current findings are very important. Increasing anti-inflammatory proteins and/or lowering inflammatory proteins in the stroke-lesioned brain is a promising way to avoid secondary damage to the brain after a stroke has occurred, and will lead to reductions in stroke-related disabilities.
###
The article, “Preferential delivery of lipid-ligand conjugated DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide to ischemic brain in hyperacute stage,” was published in Molecular Therapy at DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.01.016
Journal
Molecular Therapy
DOI
10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.01.016
Article Title
Preferential delivery of lipid-ligand conjugated DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide to ischemic brain in hyperacute stage




