Note: Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers Deok-Ho Kim and Devin Mair will participate in a NASA teleconference for journalists on Tuesday, March 14, at 11 a.m. ET.
Credit: Deok-Ho Kim and Devin Mair, Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Note: Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers Deok-Ho Kim and Devin Mair will participate in a NASA teleconference for journalists on Tuesday, March 14, at 11 a.m. ET.
Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers are collaborating with NASA to send human heart “tissue-on-a-chip” specimens into space as early as March. The project is designed to monitor the tissue for changes in heart muscle cells’ mitochondria (their power supply) and ability to contract in low-gravity conditions.
The tissue samples will be launched into space aboard SpaceX CRS-27, a resupply mission to the International Space Station, slated for liftoff no earlier than Tuesday, March 14, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Astronauts on board during the mission will also introduce three FDA-approved medicines to the samples in efforts to prevent heart cell changes known or suspected to occur in those undertaking long-duration spaceflights.
“It’s possible that what we learn from these experiments in space could also inform how we treat age-related cardiac problems,” says Deok-Ho Kim, Ph.D., professor of biomedical engineering at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, because many heart cellular changes already detected in space explorers mimic changes linked to heart muscle aging in general.
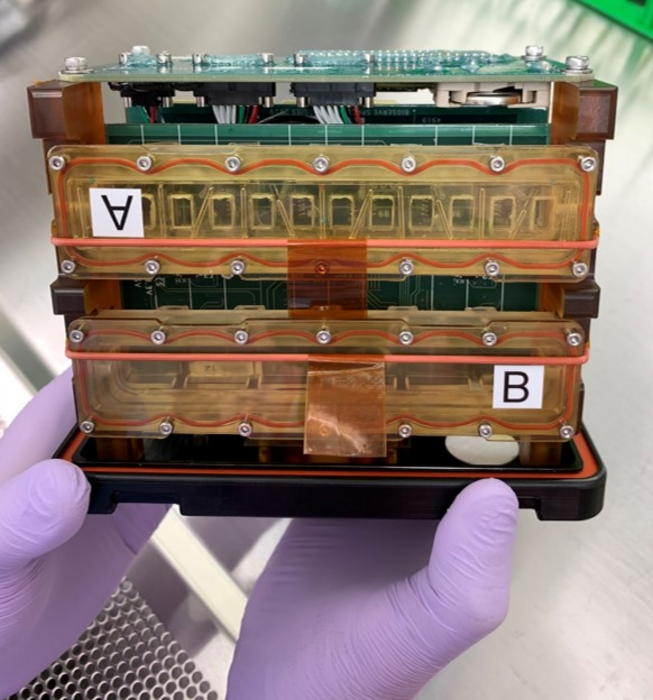
To develop the microengineered human heart tissue-on-a-chip, researchers begin with human induced pluripotent stem cells grown in the laboratory. Such cells are able to develop into nearly any type of cell, and are coaxed biologically to develop into beating human cardiomyocytes, the muscle cells that make hearts contract.
Groups of cardiomyocytes form tissue that can be strung between two posts, one flexible and one stiff. The flexible post has an embedded magnet and, when placed over sensors, allows for collection of information on tissue contraction. The chamber enclosing the tissue is sealed so that liquid media feeding the tissue doesn’t float away in space. These tissue chambers are then loaded into so-called plate habitats with the magnetic sensors located beneath the tissue. The experimental payload consists of two of these plate habitats, which measure about 7 inches long, 5 inches tall and 4 inches wide.
Kim, his previous postdoctoral researcher Jonathan Tsui, and his doctoral student Devin Mair previously sent heart tissue into space in March 2020. Those experiments, presented at the Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine International Society-Americas 2022 Annual Meeting, showed that microgravity in space changed the cells’ mitochondria and the tissues’ ability to contract.
In the new experiments with their microengineered human heart tissues-on-a-chip, the scientists will focus on the proteins activated during tissue inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction.
The astronauts aboard the space station will also test whether any of three medicines can stave off the problems anticipated in space-bound heart cells.
Funding for the research was provided by the National Institutes of Health (UH3TR003519).




