Genetic information encoded in genomic DNA is transcribed to mRNAs and then the codons on mRNA are decoded by transfer RNAs (tRNAs) during protein synthesis. tRNAs deliver amino acids to ribosomes and proteins are synthesized from the amino acids on the ribosomes according to the decoded genetic information. Therefore, tRNA plays a key role during the translation of genetic information. tRNAs contain numerous modified nucleosides, which regulate the accuracy and efficiency of protein synthesis. Modified nucleosides in tRNA are synthesized by tRNA modification enzymes. Therefore, unveiling the mechanisms by which tRNA modification enzymes selectively recognize substrate tRNAs from non-substrate RNAs; the when, where, and how many tRNAs are being modified by the modification enzymes, is of crucial importance to understand the protein synthesis machinery. Addressing these key questions is, however, challenging due to the lack of a high-throughput technique that identifies the characteristic properties of tRNA modification enzymes.
Credit: Ehime University, Ryota Yamagami, Hiroyuki Hori
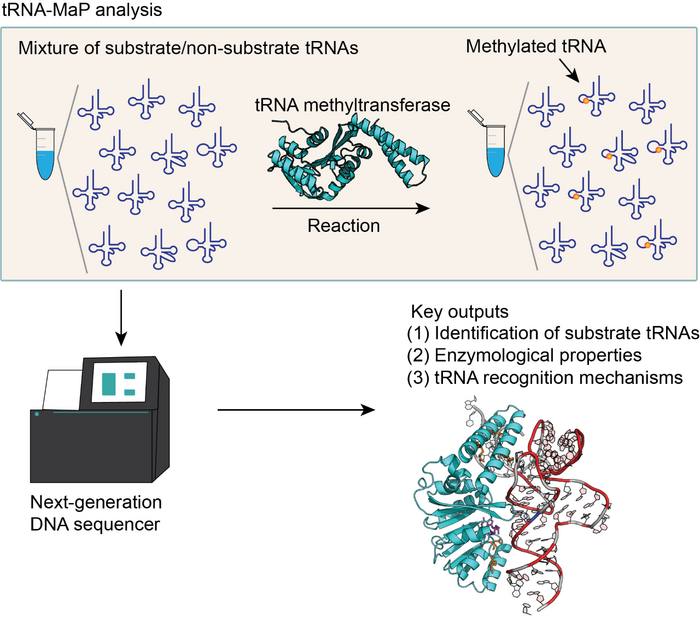
Genetic information encoded in genomic DNA is transcribed to mRNAs and then the codons on mRNA are decoded by transfer RNAs (tRNAs) during protein synthesis. tRNAs deliver amino acids to ribosomes and proteins are synthesized from the amino acids on the ribosomes according to the decoded genetic information. Therefore, tRNA plays a key role during the translation of genetic information. tRNAs contain numerous modified nucleosides, which regulate the accuracy and efficiency of protein synthesis. Modified nucleosides in tRNA are synthesized by tRNA modification enzymes. Therefore, unveiling the mechanisms by which tRNA modification enzymes selectively recognize substrate tRNAs from non-substrate RNAs; the when, where, and how many tRNAs are being modified by the modification enzymes, is of crucial importance to understand the protein synthesis machinery. Addressing these key questions is, however, challenging due to the lack of a high-throughput technique that identifies the characteristic properties of tRNA modification enzymes.
To overcome this issue, Drs. Yamagami and Hori at Ehime University applied next-generation DNA sequencing technology to functional analyses of tRNA modification enzymes and developed a new high-throughput assay method, “tRNA-MaP”. The tRNA-MaP technique can rapidly screen an RNA pool consisting of more than 5,000 RNA species and identify the substrate tRNAs of the target tRNA modification enzyme(s) with comparative sensitivity to already-established methods. By tRNA-MaP, in combination with protein orthology analyses, we predicted numerous natural modifications in Geobacillus stearothermophilus tRNAs. Furthermore, we analyzed the substrate recognition mechanism of G. stearothermophilus tRNA m1A22 methyltransferase (TrmK), which methylates adenosine at position 22 to 1-methyladenosine (m1A22) in tRNA, using tRNA-Map. Mutation profiling has revealed that TrmK selects a subset of tRNAs for the substrate. Using 240 variants of G. stearothermophilus tRNALeu transcripts, we found that U8, A14, G15, G18, G19, U55, Purine57 and A58 are important for the methylation by TrmK. In addition, based on the recognition sites in tRNA and the crystal structure of TrmK, a docking model between TrmK and tRNA has been constructed.
This study has revealed that tRNA-Map is applicable for the analysis of the tRNA modification enzyme. Notably, because tRNA-Map can analyze any RNA molecular species from any organism, even DNA molecules, tRNA-Map can be used for analysis of all nucleic acid-related proteins except for tRNA modification enzymes. Thus, tRNA-Map can accelerate the integrative understanding of the flow of genetic information.
Journal
Journal of Biological Chemistry
DOI
10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102759




