Credit: UC Riverside
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (http://www.ucr.edu) — Insects, like mammals including humans, sort chemicals by taste into a few categories and use this information to decide whether to ingest or reject food.
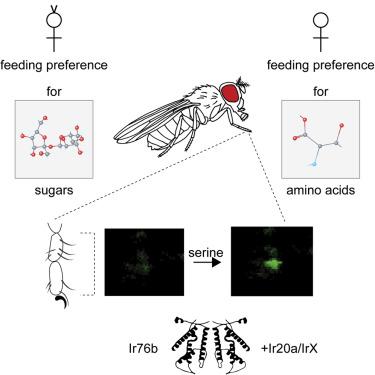
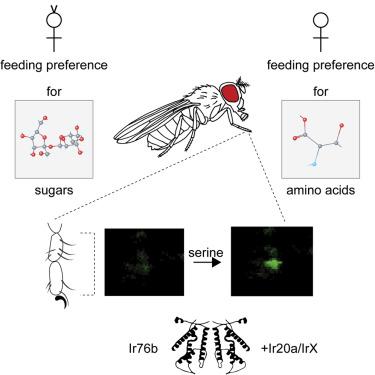
University of California, Riverside researchers have identified a receptor playing a key role in insect identification of amino acid, or umami, taste.
Amino acid or umami taste is one of the five basic taste categories in humans. There has been some evidence that insects also possess this taste ability, but it was not very well characterized, and the receptor proteins were not known.
The research, led by Anindya Ganguly, a graduate student in Anupama Dahanukar's laboratory, describes cellular and behavioral responses to amino acids in fruit flies, a common genetic model insect, and identifies an amino acid co-receptor, Ir76b. Dahanukar is an associate professor of entomology.
Ir76b is a highly conserved receptor found in all insects. Its role in amino acid taste is helped by additional Ir receptors, which may offer possible targets for identifying compounds that could be used to modify amino acid-stimulated feeding behaviors as part of efforts to control insect populations.
The results were published in a paper, "A molecular and cellular context-dependent role for Ir76b in detection of amino acid taste," that was recently published in the journal Cell Reports.
###
UC Riverside undergraduate students Vi-Khoi Duong, Angelina Lee, Hanni Schoniger and Erika Varady participated in the project and are co-authors on the paper, in addition to Ganguly and Lisa Pang, who was a postdoctoral researcher in Dahanukar's lab.
Media Contact
Sean Nealon
[email protected]
951-827-1287
@UCRiverside
http://www.ucr.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag