Researchers at the Max Planck Institute in Plön show that reputation plays a key role in determining which rewarding policies people adopt. Using game theory, they explain why individuals learn to use rewards to specifically promote good behaviour.
Credit: MPI for Evolutionary Biology
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute in Plön show that reputation plays a key role in determining which rewarding policies people adopt. Using game theory, they explain why individuals learn to use rewards to specifically promote good behaviour.
Often, we use positive incentives like rewards to promote cooperative behaviour. But why do we predominantly reward cooperation? Why is defection rarely rewarded? Or more generally, why do we bother to engage in any form of rewarding in the first place? Theoretical work done by researchers Saptarshi Pal and Christian Hilbe at the Max Planck Research Group ‘Dynamics of Social Behaviour’ suggests that reputation effects can explain why individuals learn to reward socially.
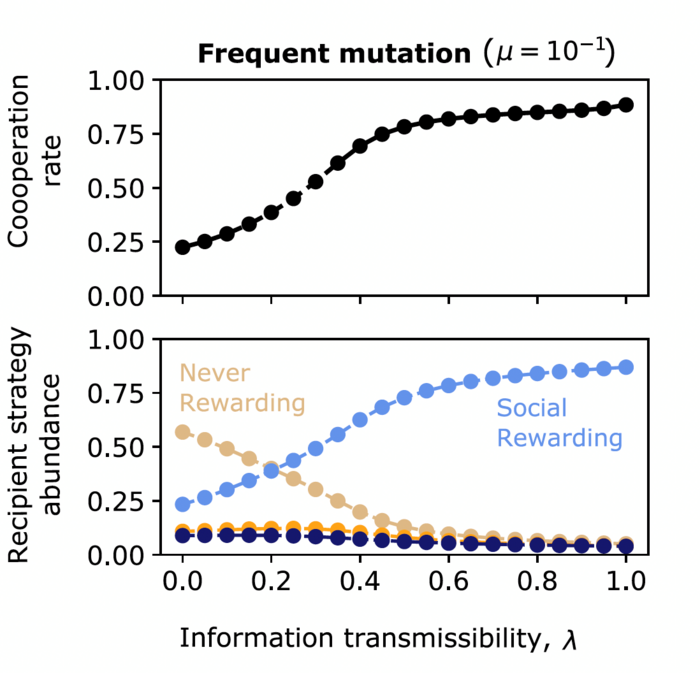
With tools from evolutionary game theory, the researchers construct a model where individuals in a population (the players) can adopt different strategies of cooperation and rewarding over time. In this model, the players’ reputation is a key element. The players know, with a degree of certainty (characterized by the information transmissibility of the population), how their interaction partners are going to react to their behaviour (that is, which behaviours they deem worthy of rewards). If the information transmissibility is sufficiently high, players learn to reward cooperation. In contrast, without sufficient information about peers, players refrain from using rewards. The researchers show that these effects of reputation also play out in a similar way when individuals interact in groups with more than two individuals.
Antisocial rewarding
In addition to highlighting the role of reputation in catalyzing cooperation and social rewarding, the scientists identify a couple of scenarios where antisocial rewarding may evolve. Antisocial rewarding either requires populations to be assorted or rewards to be mutually beneficial for both the recipient and the provider of the reward. “These conditions under which people may learn to reward defection are however a bit restrictive since they additionally require information to be scarce” adds Saptarshi Pal.
The results from this study suggest that rewards are only effective in promoting cooperation when they can sway individuals to act opportunistically. These opportunistic players only cooperate when they anticipate a reward for their cooperation. A higher information transmissibility increases both, the incentive to reward others for cooperating, and the incentive to cooperate in the first place. Overall, the model suggests that when people reward cooperation in an environment where information transmissibility is high, they ultimately benefit themselves. This interpretation takes the altruism out of social rewarding – people may not use rewards to enhance others’ welfare, but to help themselves.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-022-33551-y
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Reputation effects drive the joint evolution of cooperation and social rewarding.
Article Publication Date
7-Oct-2022




