Premature ovarian ageing (POA) refers to an early decline in ovarian function; it is the main cause of infertility in elder women and is characterized by a markedly reduced ovarian reservoir. An interesting review summarized that women born in famine have a significantly earlier menopausal age, which indicates that the neonatal nutrition condition is important to determine follicular reserve and the age of natural menopause. However, the relationship between nutritional conditions during early-life and female reproductive function in adulthood, as well as the specific mechanism, is largely unknown.
Credit: Xin-Ying Wang, Xin-Ge Zhang, Yong-Juan Sang, Dan-Yang Chong, Xiao-Qiang Sheng, Hai-Quan Wang, Chao-Fan Yang, Gui Jun Yan, Hai-Xiang Sun, Chao-Jun Li
Premature ovarian ageing (POA) refers to an early decline in ovarian function; it is the main cause of infertility in elder women and is characterized by a markedly reduced ovarian reservoir. An interesting review summarized that women born in famine have a significantly earlier menopausal age, which indicates that the neonatal nutrition condition is important to determine follicular reserve and the age of natural menopause. However, the relationship between nutritional conditions during early-life and female reproductive function in adulthood, as well as the specific mechanism, is largely unknown.
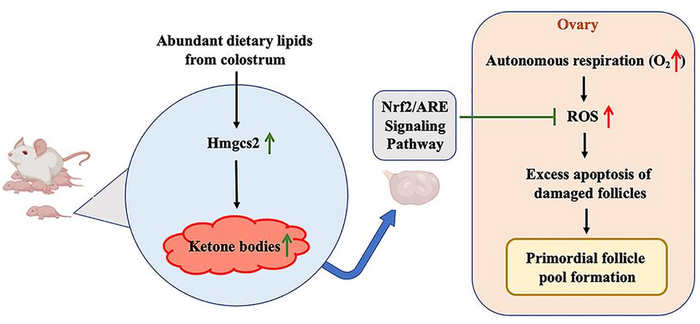
Scientists from the State Key Laboratory for Reproductive Medicine of Nanjing Medical University and Reproductive Medicine Center of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital found that neonatal serum ketone body production could determine the quantity and quality of the primordial follicle pool by reducing ROS-induced primordial follicle apoptosis during follicular reserve formation in the early life. This study entitled “The neonatal ketone body is important for primordial follicle pool formation and regulates ovarian ageing in mice” is published online in Life Metabolism on August 2022.
The newborns are exposed to rich dietary lipids from colostrum, which transiently stimulate high expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (Hmgcs2), the rate-limiting enzyme in most of organs including ovary in neonatal mice. Thus, the neonatal serum ketone body level is significantly higher than adulthood. When Hmgcs2 gene is deleted, the neonatal ketone body level is largely decrease, which perfectly mimic the malnutrition related ketone body deficiency in newborn mice. Using this ideal animal model, they found that ketone body deficiency in neonatal mice resulted in smaller ovarian follicle reservoir because of the increased apoptosis of primordial follicles, which further led to POA indicated by gradually decreased litter size and prolonged litter interval.
Another challenge the newborns faced is higher oxidative stress because of spontaneous breathing. The ROS production in Hmgcs2 deficient ovary was highly elevated, which led to severe DNA damage of primordial follicle, thus induced excessive apoptosis of primordial follicles. They further confirmed that β-Hydroxybutyrate (β-HB), supplementation in Hmgcs2 knockout mice could reduce ROS production and alleviate DNA damage induced apoptosis of primordial follicle. Thus, the authors demonstrated that the neonatal ketone body could maintain the quantity and quality of the primordial follicle pool by decreasing ROS production.
To summarize, this report elucidates that infant nutrition situation and related neonatal ketone body production play an important role in the formation of the primordial follicle pool and further affect the normal ovarian capacity in adulthood. This study provides a new metabolic explanation for POA and provides new possible strategies to improve the follicular reservoir during early life.
###
Reference: Xin-Ying Wang et al. (2022). The neonatal ketone body is important for primordial follicle pool formation and regulates ovarian ageing in mice. Life Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1093/lifemeta/loac017
About Higher Education Press
Founded in May 1954, Higher Education Press Limited Company (HEP), affiliated with the Ministry of Education, is one of the earliest institutions committed to educational publishing after the establishment of P. R. China in 1949. After striving for six decades, HEP has developed into a major comprehensive publisher, with products in various forms and at different levels. Both for import and export, HEP has been striving to fill in the gap of domestic and foreign markets and meet the demand of global customers by collaborating with more than 200 partners throughout the world and selling products and services in 32 languages globally. Now, HEP ranks among China’s top publishers in terms of copyright export volume and the world’s top 50 largest publishing enterprises in terms of comprehensive strength.
The Frontiers Journals series published by HEP includes 28 English academic journals, covering the largest academic fields in China at present. Among the series, 13 have been indexed by SCI, 6 by EI, 2 by MEDLINE, 1 by A&HCI. HEP’s academic monographs have won about 300 different kinds of publishing funds and awards both at home and abroad.
About Life Metabolism
Life Metabolism is a fully open access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes one volume per year online, providing a platform for the publication of works of high significance and broad interest in all areas of metabolism. Life Metabolism welcomes several different article types, including original article, review article, research highlight, letter, editorial, perspective, and so on. Once a paper is accepted, Life Metabolism can publish a precopyedited, preproofed version of the paper online within 48 hours of receiving a signed licence, and this will be replaced by a copyedited, proofed version of the paper as soon as it is ready. The Editors-in-Chief are professors Peng Li at Tsinghua University and John R Speakman at University of Aberdeen, UK.
Journal
Life Metabolism
DOI
10.1093/lifemeta/loac017
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animal tissue samples
Article Title
The neonatal ketone body is important for primordial follicle pool formation and regulates ovarian ageing in mice
Article Publication Date
11-Aug-2022




