Tokyo, Japan – Inflammatory myopathies can be challenging to treat, but a new study reports encouraging findings for patients with these debilitating conditions. Researchers from Japan have found that a novel member of a class of anti-diabetes drugs could be the key to treating patients with muscle wasting disease.
Credit: Department of Rheumatology, TMDU
Tokyo, Japan – Inflammatory myopathies can be challenging to treat, but a new study reports encouraging findings for patients with these debilitating conditions. Researchers from Japan have found that a novel member of a class of anti-diabetes drugs could be the key to treating patients with muscle wasting disease.
In a study published in June in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) reveal that a novel member of a class of medications that is already clinically approved for use in patients with diabetes may also be effective for treating patients with polymyositis (PM).
PM is an immune-mediated muscle disease that starts off as muscle weakness and progresses to significant disability. Glucocorticoids, the main medication used to treat PM, suppress the muscle injury caused by inflammation, but can also cause damage to the muscle themselves, leading to persistent muscle weakness.
“There is a clear need for new therapeutic strategies for these patients that not only suppress inflammation, but also help maintain and restore muscle strength,” states Mari Kamiya, first author on the study. “We hypothesized that a class of drugs known as GLP-1R agonists, which have anti-inflammatory effects and suppress muscle wasting, could be beneficial in this context.”
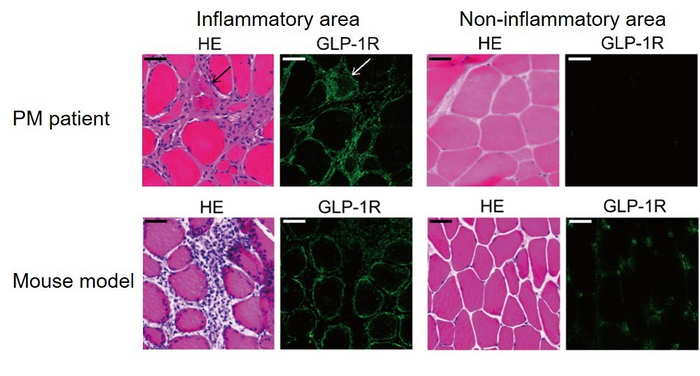
To test this, the researchers first determined whether the GLP-1R is expressed on muscle fibers affected in PM by analyzing muscle specimens from patients with PM as well as a mouse model of PM. They then assessed the effect of treatment with PF1801, a novel GLP-1R agonist.
“The results were very striking,” says Shinsuke Yasuda, senior author of the study. “GLP-1R was strongly expressed on inflamed muscle fibers in the samples from both patients and the animal model , and treating mice with PF1801 suppressed muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, and muscle inflammation.”
Importantly, treatment with PF1801 also decreased the levels of inflammatory mediators in the muscle environment. Further investigation of the underlying mechanisms showed that PF1801 suppressed muscle fiber death, or necroptosis, and the subsequent release of inflammatory mediators through multiple pathways.
“Our findings suggest that PF1801 could be used to suppress muscle inflammation and improve muscle strength in patients with PM,” states Kamiya.
Given that GLP-1R agonists may be also beneficial for treating conditions such as skin disease, heart disease, and arthritis, PF1801 could potentially help improve other symptoms associated with inflammatory myopathies. GLP-1R agonists are already approved for use in patients with diabetes and have known safety profiles, so if its effectiveness against PM is demonstrated in clinical trials, PF1801 could be approved rapidly for this new application.
###
The article, “Amelioration of inflammatory myopathies by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist via suppressing muscle fibre necroptosis,” was published in Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle at DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.13025.
Journal
Journal of Cachexia Sarcopenia and Muscle
DOI
10.1002/jcsm.13025
Article Title
Amelioration of inflammatory myopathies by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist via suppressing muscle fibre necroptosis




