Researchers have discovered that the manner of walking, or gait, of Japanese children develops differently from that of children in other countries.
Credit: Tadashi Ito, Reiko Matsushita
Researchers have discovered that the manner of walking, or gait, of Japanese children develops differently from that of children in other countries.
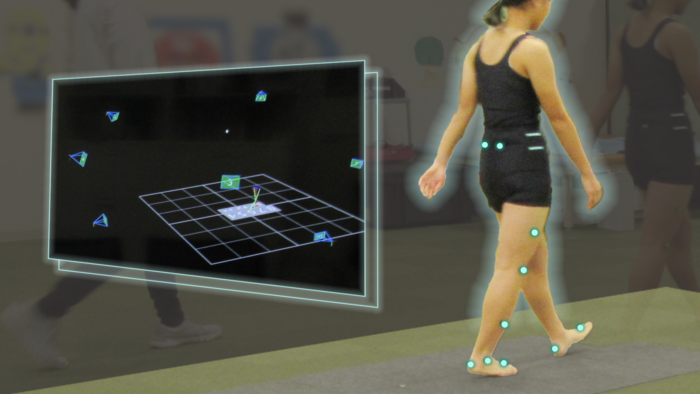
Gait is a complex, unconscious motor pattern, essential for most daily activities. It comprises a sequence of movements that involve the hip, knee, and foot. From a medical point of view, a person’s gait is critical to measuring their quality of life and health status. Researchers seek to understand the forces involved in gait to help treat people with movement disorders. However, in Japan, data on age-related gait parameters among children are limited.
A group of researchers, including Tadashi Ito and Hideshi Sugiura in the Department of Integrated Health Sciences at Nagoya University, and Koji Noritake and Nobuhiko Ochi at the Aichi Prefectural Mikawa Aoitori Medical and Rehabilitation Center for Developmental Disabilities, determined the normative gait pattern of Japanese children. They used a 3D gait analysis system to investigate age-related differences in lower limb movements during walking. Reporting their findings in Scientific Reports, the group found that the recorded gait of Japanese elementary school children differed by age. Although the gait patterns and gait parameters of typical Japanese children aged 6-12 are similar to those of children in other developed countries, their development differs.
Dr. Ito and his colleagues found four important differences among age groups. First, there was an increase in cadence, the number of steps performed in one minute, among children in the 11–12-year-old group compared to the 6-8 year group. Second, there was also a decrease in step and stride length among children aged 11–12 years compared to those aged 9–10 years. Third, children 11-12 years had less range of motion of the knee during the gait cycle. Fourth, as children aged, a higher plantarflexion moment was observed, which is the motion when you point your toes at the start of the walking movement.
“We believe that differences in lifestyle, build, and cultural factors all affect Japanese children’s gait,” said Dr. Ito. “This is not likely to affect the health of Japanese children. But it does indicate characteristics different from those of children in other countries. These results provide an important tool for assessing normal and pathological gait and can determine the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment and rehabilitation for gait disorders.“
There was no acquisition of funding for this study.
Journal
Scientific Reports
DOI
10.1038/s41598-022-11906-1




