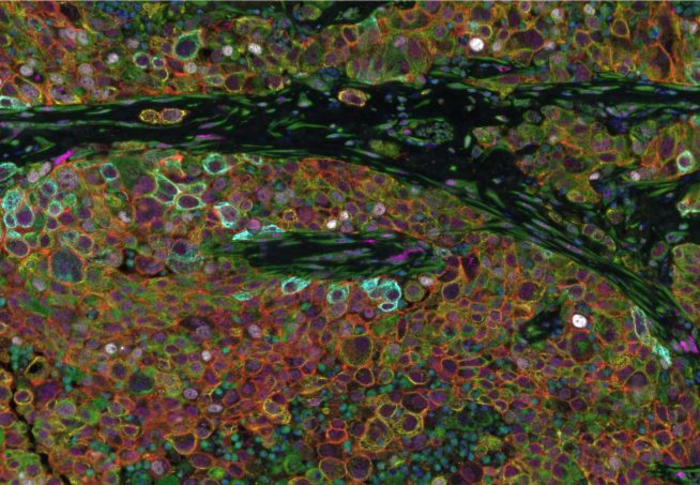
LEBANON, NH – Tumor heterogeneity refers to the presence of a variety of distinct cell types within a tumor. High tumor heterogeneity is thought to contribute to breast cancer progression and metastasis, or spreading to other parts of the body. Researchers at Dartmouth Cancer Center have developed a new approach for detecting and quantifying tumor heterogeneity to assess patient outcomes in breast cancer. The approach will pave the way to utilizing the extent of tumor heterogeneity as a factor in therapeutic decision-making.
Credit: Diwakar R. Pattabiraman
LEBANON, NH – Tumor heterogeneity refers to the presence of a variety of distinct cell types within a tumor. High tumor heterogeneity is thought to contribute to breast cancer progression and metastasis, or spreading to other parts of the body. Researchers at Dartmouth Cancer Center have developed a new approach for detecting and quantifying tumor heterogeneity to assess patient outcomes in breast cancer. The approach will pave the way to utilizing the extent of tumor heterogeneity as a factor in therapeutic decision-making.
The study finds that high levels of heterogeneity in a patient’s tumor are typically associated with poor prognosis. However, they were also able to identify specific proteins that regulate the extent of heterogeneity in a tumor and its potential to spread.
These findings, “Phenotypic heterogeneity driven by plasticity of the intermediate EMT state governs disease progression and metastasis in breast cancer” are newly published in Science Advances.
“This work is exciting because we have developed an approach to quantify tumor heterogeneity that can be applied to patient specimens obtained in a pathology lab,” says corresponding author Diwakar R. Pattabiraman, PhD.
Recognizing the impact of tumor heterogeneity and developing ways of quantifying it, are the initial steps to ultimately being able to decrease or curtail the development of high levels of heterogeneity in patient tumors as a therapeutic avenue.
The team’s next steps are to assess how the extent of tumor heterogeneity determines treatment outcomes in breast cancer. “If we can obtain tumor specimens from a patient before therapy, we can try to predict how they respond to the current standard-of-care regimens,” says Pattabiraman.
The team’s work was presented in April, 2022, at the American Association for Cancer Research annual meeting in New Orleans, LA by Dr. Meredith Brown, a recent graduate of the Pattabiraman laboratory who led the research study.
* * *
Diwakar R. Pattabiraman, PhD, is a member of the Cancer Signaling, Genomes and Networks Research Program at Dartmouth Cancer Center, and Assistant Professor of Molecular and Systems Biology at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine. His research interests include studying the sources of tumor heterogeneity and its implications for tumor progression and therapy resistance. @diwraman
Meredith S. Brown, PhD, is a recent graduate of the Pattabiraman laboratory and the Molecular and Cellular Biology graduate program at Dartmouth. In addition to understanding the biology of breast tumor heterogeneity, her primary project has focused on developing the methodology and application of a novel assay to quantify tumor heterogeneity as a tool to assess patient prognosis.
* * *
About Dartmouth Cancer Center
About Dartmouth Cancer Center: Dartmouth Cancer Center combines the advanced cancer research in partnership with Dartmouth and the Geisel School of Medicine, with award-winning, personalized, and compassionate patient-centered cancer care based at the Norris Cotton Cancer Care Pavilion at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center. With 14 locations around New Hampshire and Vermont, Dartmouth Cancer Center is one of only 52 National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Centers. Each year the Dartmouth Cancer Center schedules 74,000 appointments seeing more than 4,500 newly diagnosed patients, and currently offers patients more than 240 active clinical trials. Celebrating its 50th anniversary in 2022, Dartmouth Cancer Center remains committed to excellence, outreach and education. We strive to prevent and cure cancer, enhance survivorship and to promote cancer health equity through pioneering interdisciplinary research and collaborations. Learn more at http://cancer.dartmouth.edu.
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.abj8002
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Phenotypic heterogeneity driven by plasticity of the intermediate EMT state governs disease progression and metastasis in breast cancer
Article Publication Date
3-Aug-2022




