Chinese researchers recently reported an innovative mechanical process for controllably exfoliating hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets (h-BNNSs).
This method, known as the “water-icing triggered exfoliation process,” was proposed by Prof. ZHANG Junyan’s group from the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
Credit: Image by LICP
Chinese researchers recently reported an innovative mechanical process for controllably exfoliating hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets (h-BNNSs).
This method, known as the “water-icing triggered exfoliation process,” was proposed by Prof. ZHANG Junyan’s group from the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
h-BNNSs, with a honeycomb-like structure similar to graphene, show excellent chemical and physical properties, such as high thermal conductivity, good resistance to oxidation, remarkable mechanical strength, a low dielectric constant, outstanding lubricity, excellent biocompatibility, and optical properties.
Due to these characteristics, h-BNNSs are promising materials for various applications, including high-performance electronic devices, dielectric substrates, thermal management, lubrication, sensors, catalysts, and sorbents. As a result, developing a simple, controllable, and scalable method to produce high-quality h-BNNSs for commercial applications is an urgent need.
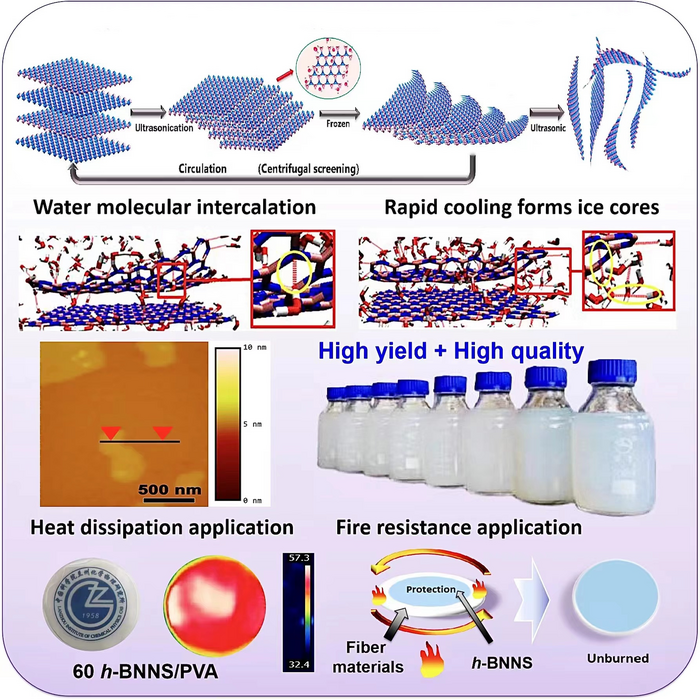
In their new research, ZHANG and his team proposed a scalable and controllable approach to exfoliate high-quality h-BNNSs from h-BN flakes.
“This method relies on efficient reduction of h-BNNS interlayer interaction by rapid volume expansion of water in icing,” said ZHANG.
Generally, h-BNNSs can be prepared using a process of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and physical exfoliation. CVD can produce wafer-scale, single-crystal monolayer h-BNNSs while the physical exfoliation process can achieve scalable production of small-sized h-BNNSs.
Based on molecular dynamics simulations, the researchers suggested that -OH groups can cause local structural distortion in the defects/edges of h-BN flakes to form an “entrance” for water molecules coming into the h-BNNS interlayer. This in turn presents a sufficient number of relatively long-lived hydrogen bonds that can generate fairly compact initial nuclei for ice nucleation.
The initial nuclei then slowly change in shape and size until they reach a stage that allows rapid expansion as the temperature drops sharply. This results in an increase in interlayer spacing and reduction of interlayer forces between adjacent h-BNNS layers as well as efficient exfoliation of h-BNNSs during subsequent ultrasonication.
“By adjusting the parameters, this exfoliation process can be used to produce large quantities of different high-quality h-BNNSs,” said Dr. AN Lulu, first author of the study.
“This method offers an environmentally friendly method to exfoliate h-BNNSs with controllable thickness by a rapid water freezing and subsequent ultrasonication process. These as-obtained h-BNNSs can be used as polymer additives, thermal conductive fillers, and flame retardants,” said Prof. YU Yuanlie, corresponding author of the study.
This study was published online in Cell Reports Physical Science and funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Foundation of LICP, CAS, and the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province.
Journal
Cell Reports Physical Science
DOI
10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.100941
Article Title
Water-icing-triggered scalable and controllable exfoliation of hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets




