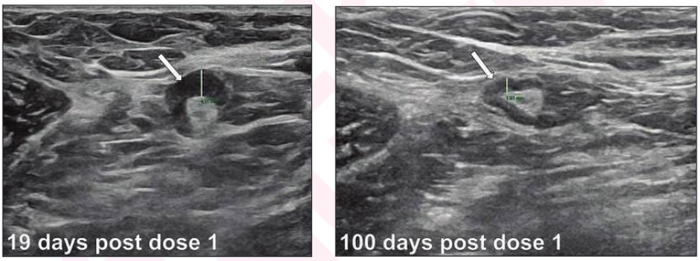
Leesburg, VA, May 19, 2022—According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), axillary lymphadenopathy detected by breast ultrasound after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination lasts longer than reported in initial vaccine clinical trials.
Credit: American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS), American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR
Leesburg, VA, May 19, 2022—According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), axillary lymphadenopathy detected by breast ultrasound after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination lasts longer than reported in initial vaccine clinical trials.
“The prolonged resolution time supports a follow-up interval of at least 12 weeks for suspected vaccine-related lymphadenopathy and avoidance of delaying screening mammography after vaccination,” wrote corresponding author Michele B. Drotman, MD.
Drotman and the Weill Cornell Medicine team extracted health record data for 111 patients (mean age, 52 years) with unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to administration of Pfizer or Moderna COVID-19 vaccine—performed within 8 weeks prior and detected on breast ultrasound (January 1–October 1, 2021) that underwent follow-up ultrasound examinations at 4–12 weeks.
In this single-center study, axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to COVID-19 mRNA vaccination resolved after a mean of 97 days since detection by breast imaging and 127 days since the first dose. Longer times to resolution were observed with Moderna (rather than Pfizer) vaccination, receipt of second dose after presentation, and thicker cortical thickness at presentation.
“The presence of subclinical lymphadenopathy and the long resolution time of lymphadenopathy,” the authors of this AJR article noted, “should reassure radiologists and patients when lymph nodes suspected to be vaccine-related persist over multiple visits.”
North America’s first radiological society, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) remains dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of medical imaging and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in radiology since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with the world’s longest continuously published radiology journal—American Journal of Roentgenology—the ARRS Annual Meeting, InPractice magazine, topical symposia, myriad multimedia educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
Journal
American Journal of Roentgenology
DOI
10.2214/AJR.22.27687
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Time for resolution of COVID-19 vaccine-related lymphadenopathy and associated factors
COI Statement
N/A




