The presence of dendritic cells, so-called ‘sentinel’ immune cells, is vital to maintain and regulate the balance of the body’s immune response. Researchers have discovered an essential role of these cells in the treatment of cancer and severe viral infections.
Credit: Würzburg Institute of Systems Immunology, Max-Planck Research Group.
The presence of dendritic cells, so-called ‘sentinel’ immune cells, is vital to maintain and regulate the balance of the body’s immune response. Researchers have discovered an essential role of these cells in the treatment of cancer and severe viral infections.
Chronic viral infections and cancers can cause a permanent impairment to the immune system, reducing the ability of immune killer T cells to remove tumour cells, or those infected by a virus – this is referred to as ‘immune exhaustion’.
Blocking immune exhaustion through drugs, such as checkpoint inhibitors, has proven to be a very powerful therapy for some cancers, but these immunotherapies do not always work and may cause severe side-effects.
Published today in Immunity, the Würzburg University-led study completed in collaboration with the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), has gained a deeper understanding of how killer T cells work with dendritic cells in the processes that drive immune exhaustion and how checkpoint inhibitors work to restore immune function.
Würzburg University Professor Wolfgang Kastenmüller, senior author and Director of the Würzburg Institute of Systems Immunology and leader of the Max-Planck Research group, said most immune exhaustion research focused on killer T cells, but little was known about the role of their cellular interaction partners.
“Our results show that checkpoint immunotherapy works at the interface between killer T cells and dendritic cells,” Professor Kastenmüller said.
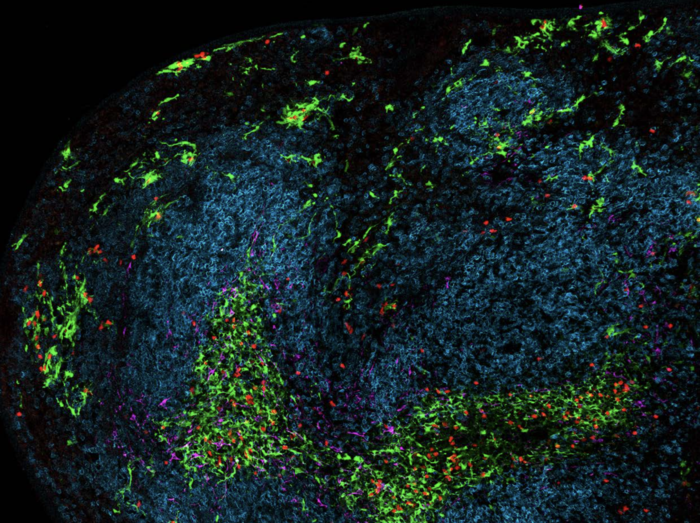
“Our study used highly sophisticated microscopy to identify where these interactions between killer T cells and dendritic cells take place and how these interactions determine the outcome of a chronic viral infection following checkpoint immunotherapy.
“We’ve shown that dendritic cells activate killer T cells just at the right level as to prevent their overactivation to avoid unwanted immunopathology. This was related to the ability of dendritic cells to maintain unique anatomical niches within lymphoid organs where killer T cells can be retained in a status ready to fight the infection at the correct moment.”
University of Melbourne Professor Sammy Bedoui, co-lead of the study and Immunology Theme Leader at the Doherty Institute said the discovery had far-reaching implications for further research into effective treatments of viral infections, such as HIV and AIDS, hepatitis, possibly COVID-19, and particular types of skin, lung or kidney cancers.
“In the absence of dendritic cells, we have shown that checkpoint inhibitors no longer work. Instead, killer T cells got out of control, resulting in more inflammation and even poorer abilities of the immune system to control the infection,” Professor Bedoui said.
This study was supported by a joint PhD program between the University of Melbourne and the University of Bonn. The project was completed in a collaboration between the Julius-Maximilians University of Würzburg, the Würzburg Institute of Systems Immunology and the Doherty Institute and the University of Melbourne.
About the Würzburg Institute of Systems Immunology, Max-Planck Research Group
The Max Planck Research Group is based at the University of Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany. They investigate the migration of leukocytes between and within organs, and investigates where and how cells of the immune system interact to achieve an effective immune response or to prevent inflammatory disease processes. The group is also investigating lymphocytes that permanently settle in different tissues and specialise in the requirements of their environment. These “local defense forces” also play a role in the regeneration of organs or the regulation of metabolic processes, for example. Using intravital multiphoton microscopy, they were recently able to clarify the early cellular events during the adaptive immune response to a virus infection. Their research group is developing new genetic tools that allow them to visualise a wide variety of specific cell types and to test their function. The goal is to understand the basic principles for a successful immune response against infectious agents and tumors and to use them therapeutically.
uni würzburg
www.med.uni-wuerzburg.de/en/systemimmunologie
About the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity
Finding solutions to prevent, treat and cure infectious diseases and understanding the complexities of the immune system requires innovative approaches and concentrated effort. This is why The University of Melbourne – a world leader in education, teaching and research excellence – and The Royal Melbourne Hospital – an internationally renowned institution providing outstanding care, treatment and medical research – have partnered to create the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute); a centre of excellence where leading scientists and clinicians collaborate to improve human health globally.
doherty.edu.au
Journal
Immunity
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
cDC1 maintain and guide the differentiation of precursors of exhausted T cells in distinct cellular niches
Article Publication Date
1-Apr-2022




