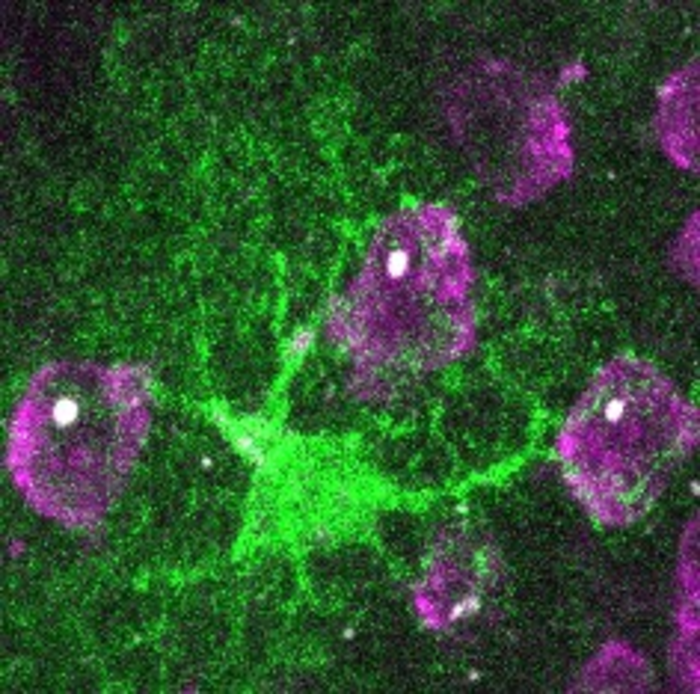
Huntington’s disease1 is caused by a mutation in the Huntingtin gene, a protein necessary for the proper functioning of several brain cells. Mutated, it is no longer able to perform properly: it can even become toxic for the neurons, triggering a defence mechanism in the brain. In turn, the astrocytes, the neurons’ support cells, change their behaviour and become “reactive”. These reactive astrocytes were traditionally considered as being deleterious to the brain because they aggravate the symptoms of other brain diseases, such as Alzheimer’s. However, in a recent study published in the journal Brain on 17 March 2022, a research team2, led by a CNRS researcher, revealed that stimulating the formation of reactive astrocytes in mouse models promotes the elimination of the mutated protein by reducing the quantity and size of its aggregates. These results show that reactive astrocytes actually cooperate with neurons in Huntington’s disease. The researchers now want to identify how to selectively stimulate these reactive astrocytes, paving the way for possible treatments.
Credit: © Laurene Abjean
Huntington’s disease1 is caused by a mutation in the Huntingtin gene, a protein necessary for the proper functioning of several brain cells. Mutated, it is no longer able to perform properly: it can even become toxic for the neurons, triggering a defence mechanism in the brain. In turn, the astrocytes, the neurons’ support cells, change their behaviour and become “reactive”. These reactive astrocytes were traditionally considered as being deleterious to the brain because they aggravate the symptoms of other brain diseases, such as Alzheimer’s. However, in a recent study published in the journal Brain on 17 March 2022, a research team2, led by a CNRS researcher, revealed that stimulating the formation of reactive astrocytes in mouse models promotes the elimination of the mutated protein by reducing the quantity and size of its aggregates. These results show that reactive astrocytes actually cooperate with neurons in Huntington’s disease. The researchers now want to identify how to selectively stimulate these reactive astrocytes, paving the way for possible treatments.
Notes
1 Huntington’s disease is a rare hereditary disease that induces significant motor, cognitive and psychiatric disorders. It is caused by neuronal degeneration that progressively worsens until the patient dies. To date, there is no known cure.
2 The teams include researchers from the Laboratoire des maladies neurodégénératives : mécanismes, thérapies, imagerie (CNRS/CEA/Université Paris Saclay), the Centre national de recherche en génomique humaine (CEA/Université Paris Saclay) and GenoSplice technology.
Journal
Brain
DOI
10.1093/brain/awac068
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Reactive astrocytes promote proteostasis in Huntington’s disease through the JAK2-STAT3 pathway
Article Publication Date
17-Mar-2022




