Oncotarget published “The protective role of prolyl oligopeptidase (POP) inhibition in acute lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion” which reported that intestinal ischemia-reperfusion develops when the blood flow to the intestines decreases, followed by the reestablishment of the blood supply to the ischemic tissue, resulting in intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction, with consequent severe local and systemic inflammation.
Credit: Correspondence to – Irene Paterniti – [email protected]
Oncotarget published “The protective role of prolyl oligopeptidase (POP) inhibition in acute lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion” which reported that intestinal ischemia-reperfusion develops when the blood flow to the intestines decreases, followed by the reestablishment of the blood supply to the ischemic tissue, resulting in intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction, with consequent severe local and systemic inflammation.
The aim of the present study is to assess the effects of POP-inhibition mediated by KYP-2047 treatment in the pathophysiology of ALI following II/R. KYP-2047 treatment ameliorated histological alteration in ileum and lung, reduced collagen amount and lowered inflammatory protein levels.
Dr. Irene Paterniti from The University of Messina said, “Ischemic process causes a lack of oxygen supply and nutrients and the following restoration of blood circulation, called reperfusion, results in oxidative tissue damage and invasion of inflammatory mediators to neighboring organs.“
Intestinal ischemia-reperfusion is a common route for many disorders, including enterocolitis, midgut volvulus, intussusception, intestinal obstruction, sepsis and hemodynamic shock. II/R damage takes over when the decrease of blood flow in the intestine is followed by the restoration of blood required to the ischemic area, resulting in severe local and systemic inflammation which spreads to nearby organs. Acute lung injury represents the most serious complication after intestinal I/R. ALI is a medical condition characterized by widespread organ inflammation with an acute onset and, although several pathophysiologic mechanisms of ALI in II/R have been partially proposed, the basic concepts remain mostly vague.
Interestingly, II/R provokes an important inflammatory response in nearby lung tissues, evidenced by neutrophilic infiltration, amplified myeloperoxidase levels and prominent vascular permeability in the lungs. Specifically, POP itself plays a role in supporting neutrophilic inflammation and this aspect involves POP to the pathology of various lung diseases. Since the POP’s involvement in angiogenesis and inflammation has been highlighted, POP inhibitors have been developed and, between these, 4-phenyl-butanoyl-l-prolyl-2-cyanopyrrolidine appears to be the most powerful and extensively studied both in in vitro and in vivo models of inflammatory diseases. Based on these findings, the aim of the present study was to assess the beneficial outcomes of POP-inhibition in lung disease induced by an experimental mouse model of intestinal ischemia performed by SAO shock-mediated injury.
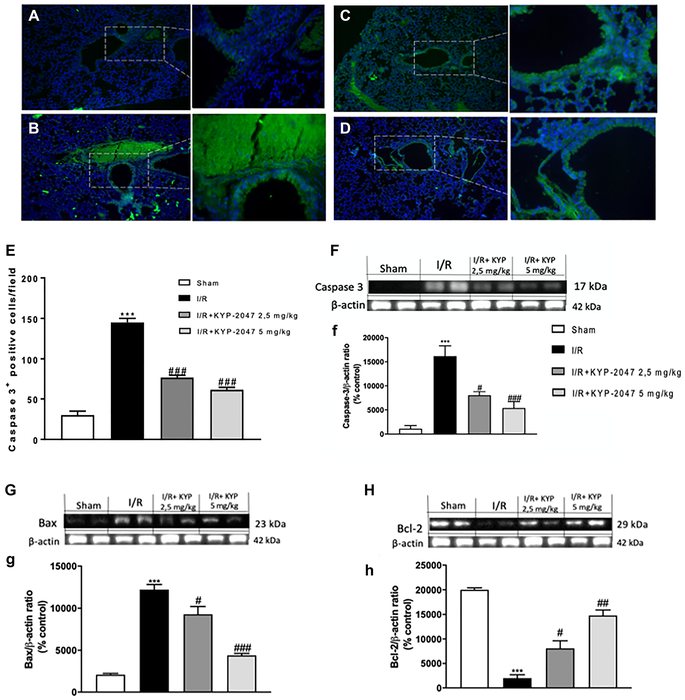
The Paterniti Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Output that they proved this apoptosis modulation also in lung following II/R, highlighting that KYP-2047 treatment acting through the activation of caspase enzymes and thus reducing apoptosis, may enhance preservation of the lung after II/R injury.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI – https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28041
Full text – https://www.oncotarget.com/article/28041/text/
Correspondence to – Irene Paterniti – [email protected]
Keywords – intestinal ischemia reperfusion (II/R), acute lung injury (ALI), prolyl oligopeptidase (POP), inflammation, angiogenesis
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud – https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter – https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn – https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest – https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit – https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957×105
Copyright © 2021 Impact Journals, LLC
Impact Journals is a registered trademark of Impact Journals, LLC
Journal
Oncotarget
DOI
10.18632/oncotarget.28041
Article Title
“The protective role of prolyl oligopeptidase (POP) inhibition in acute lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion”




