Placing a 2D Bose-Einstein condensate in the vicinity of a graphene layer confers superconductivity to the material
Credit: Institute for Basic Science
Superconductivity is a physical phenomenon where the electrical resistance of a material drops to zero under a certain critical temperature. Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory is a well-established explanation that describes superconductivity in most materials. It states that Cooper pairs of electrons are formed in the lattice under sufficiently low temperature and that BCS superconductivity arises from their condensation. While graphene itself is an excellent conductor of electricity, it does not exhibit BCS superconductivity due to the suppression of electron-phonon interactions. This is also the reason that most ‘good’ conductors such as gold and copper are ‘bad’ superconductors.
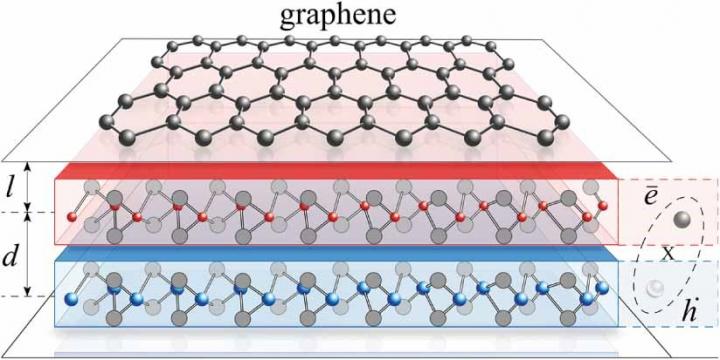
Researchers at the Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems (PCS), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea) have reported on a novel alternative mechanism to achieve superconductivity in graphene. They achieved this feat by proposing a hybrid system consisting of graphene and 2D Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC). This research is published in the journal 2D Materials.
Along with superconductivity, BEC is another phenomenon that arises at low temperatures. It is the fifth state of matter first predicted by Einstein in 1924. The formation of BEC occurs when low-energy atoms clump together and enter the same energy state, and it is an area that is widely studied in condensed matter physics. A hybrid Bose-Fermi system essentially represents a layer of electrons interacting with a layer of bosons, such as indirect excitons, exciton-polaritons, etc. The interaction between Bose and Fermi particles leads to various novel fascinating phenomena, which piques interests from both the fundamental and application-oriented perspectives.
In this work, the researchers report a new mechanism of superconductivity in graphene, which arises due to interactions between electrons and “bogolons”, rather than phonons as in typical BCS systems. Bogolons, or Bogoliubov quasiparticles, are excitation within BEC which has some characteristics of a particle. In certain ranges of parameters, this mechanism permits the critical temperature for superconductivity up to 70 Kelvin within graphene. The researchers also developed a new microscopic BCS theory which focuses specifically on the novel hybrid graphene-based system. Their proposed model also predicts that superconducting properties can be enhanced with temperature, resulting in the non-monotonous temperature dependence of the superconducting gap.
Furthermore, the research showed that the Dirac dispersion of graphene is preserved in this bogolon-mediated scheme. This indicates that this superconducting mechanism involves electrons with relativistic dispersion — a phenomenon that is not so well-explored in condensed matter physics.
“This work sheds light on an alternative way to achieve high-temperature superconductivity. Meanwhile, by controlling the properties of a condensate, we can tune the superconductivity of graphene. This suggests another channel to control the superconductor devices in the future.”, explains Ivan Savenko, the leader of the Light-Matter Interaction in Nanostructures (LUMIN) team at the PCS IBS.
###
Media Contact
William I. Suh
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




