Credit: Lindsay Lafreniere
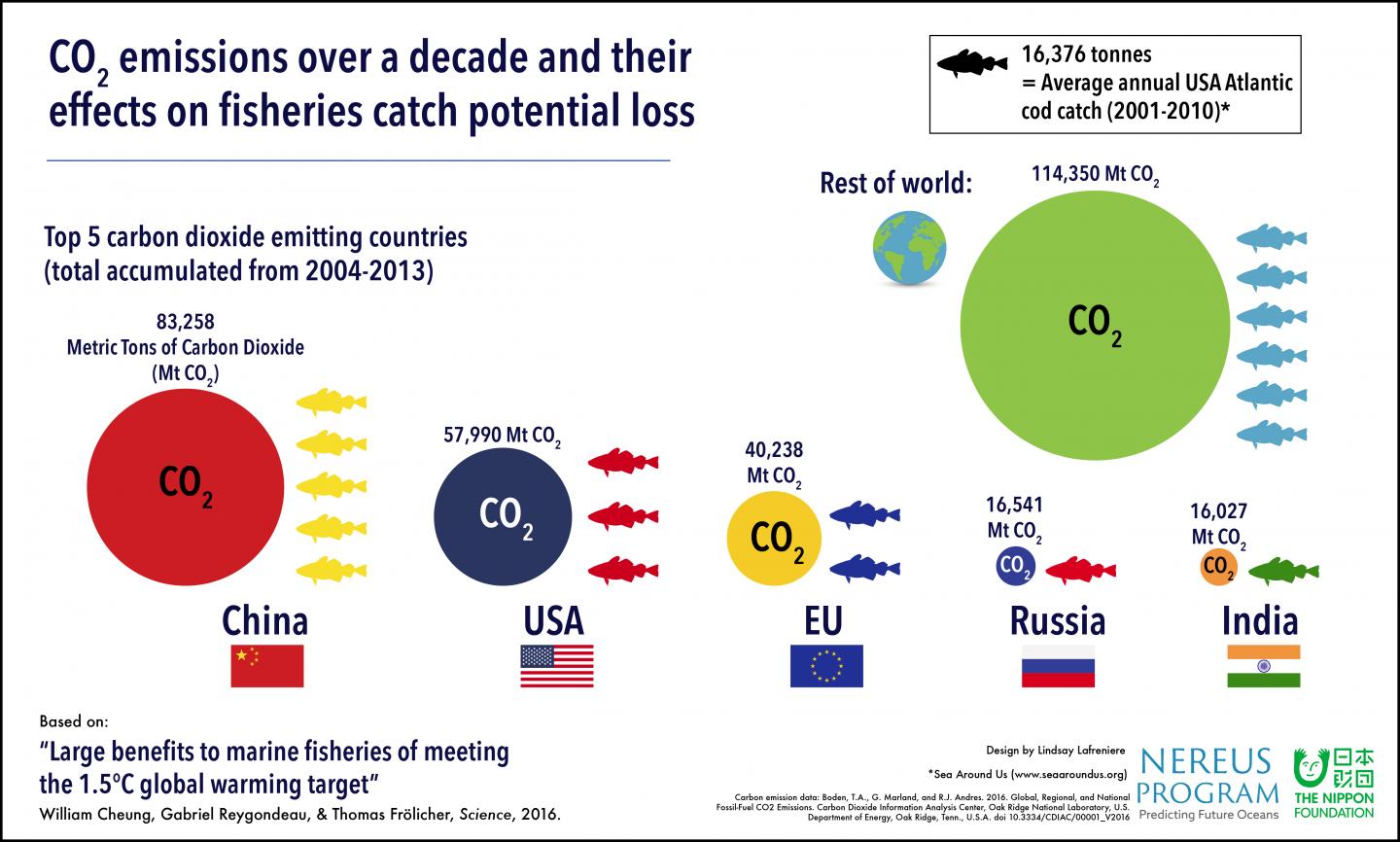
Limiting temperature increases to 1.5°C over pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement, will significantly minimize the impact of global warming on the catch potential of marine ecosystems and limit the turnover of harvested species, a new study reports. The results highlight the urgent need for the global community to adhere to the recommended target of 1.5°C, since hitting temperature increases of 3.5°C could result in an additional three-fold decline in marine biomass for the fishing industry. To better understand how different warming scenarios will impact marine ecosystems, William Cheung and colleagues analyzed data from 19 Earth system models, testing responses to situations where strong mitigation efforts are applied, or high emissions scenarios continue into the future. They applied their model to 892 species of exploited marine fishes and invertebrates. The results estimate that a warming increase of 3.5°C will decrease the maximum catch potential on a global level by 8%, compared to temperature increases of 1.5°C that will decrease maximum catch potential by 2.5%. Some regions will be hit significantly harder under the more dramatic warming condition, however; for example, the maximum catch potential may decrease as much as 47% in the Indo-Pacific region, which includes the Bay of Bengal, Gulf of Thailand, South China Sea, and Sulu-Celebes Sea. Species turnover can also vary depending on global temperatures changes, where, under 3.5°C increase conditions, species turnover is projected to be about 22% of the average species richness observed between 1950 and 1969, compared to 8% if warming is restricted to 1.5°C. The authors also highlight other region-specific projections. They note a few assumptions in their model, but emphasize that these, if anything, mean that their projections are an underestimation. A Perspective by Elizabeth A. Fulton discusses these results in greater detail.
###
Media Contact
Science Press Package
[email protected]
202-326-6440
@AAAS
http://www.aaas.org
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag