A joint research team led by Prof. FU Qiaomei from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences sequenced the ancient genomes of 31 individuals from southern East Asia, thus unveiling a missing piece of human prehistory.
The study was published in Cell on June 24.
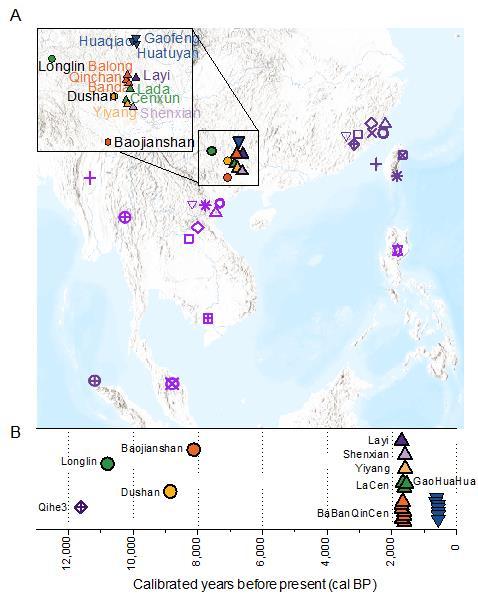
Prof. FU’s team used DNA capture techniques to retrieve ancient DNA from Guangxi and Fujian, two provincial-level regions in southern China. They sequenced genome-wide DNA from 31 individuals dating back 11,747 to 194 years ago. Of these, two date back to more than 10,000 years ago, making them the oldest genomes sampled from southern East Asia and Southeast Asia to date.
Previous ancient DNA studies showed that ~8,000-4,000-year-old Southeast Asian Hòabìnhian hunter-gatherers possessed deeply divergent Asian ancestry, whereas the first Southeast Asian farmers beginning ~4,000 years ago show a mixture of ancestry associated with Hòabìnhian hunter-gatherers and present-day southern Chinese populations. In coastal southern China, ~9,000-4,000-year-old individuals from Fujian province show ancestry not as deeply divergent as the Hòabìnhian.
In Guangxi, FU and her team’s sampling showed that the ancestry present was unlike that sampled previously in Fujian and Southeast Asia. Instead, they found a unique East Asian ancestral population (represented by the 11,000-year-old Longlin individual from Guangxi). Their findings highlight that 11,000 years ago, at least three genetically distinct ancestries composed the human landscape in southern East Asia and Southeast Asia: Fujian ancestry, Hòabìnhian ancestry, and Guangxi ancestry.
In addition to sharing Longlin ancestry, the Dushan and Baojianshan individuals in Guangxi also show strong evidence for admixture in southern China ~9,000 to 6,000 years ago. Dushan and Baojianshan were a mixture of local Guangxi ancestry, southern ancestry previously sampled in Fujian, and Deep Asian ancestry related to Southeast Asian Hòabìnhian hunter-gatherers.
Previously, it was shown that southern Chinese populations expanded to Southeast Asia, mixing with and eventually replacing Hòabìnhians in Southeast Asia. FU’s team showed that the dynamics were more complex, since populations carrying Hòabìnhian ancestry either co-existed with populations carrying Guangxi ancestry in southern China or gene flow upwards from Southeast Asia to southern China also occurred as early as ~8,000-6,000 years ago.
The study fills a research gap in the region connecting East and Southeast Asia, revealing a new genetic ancestry different from that found in coastal areas of southern China and in Southeast Asia.
Furthermore, it shows the impact of migration and admixture of populations at the crossroads of East and Southeast Asia in the last 11,000 years, revealing a long history of intermingling between these two regions.
“While we now have a better understanding of the population history in the last 11,000 years at the crossroads of East and Southeast Asia, future sampling in regions near the Yangtze River and southwest China are needed for a comprehensive understanding of the genetic history of humans in southern China,” said Prof. FU.
Genetic samples from ancient humans in these regions will likely further clarify the remarkably diverse genetic prehistory of humans in southeastern Asia, and inform the genetic shifts that occurred between 6,000 and 1,500 years ago and contributed to the genetic composition observed today in southern China.
###
Media Contact
FU Qiaomei
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.