Researchers from the Turku PET Centre and Technical University of Munich have discovered a new mechanism controlling satiation. According to the recently published study, the hormone secretin induces satiation by activating brown adipose tissue.
Brown adipose tissue is known for its ability to generate heat in response to cold exposure. Its activity has been proven to be connected to normal weight and glucose metabolism as well as lesser risks of cardiovascular diseases. Meals have also been shown to increase the thermogenesis in brown fat, but the significance of this phenomenon has been unclear.
– Secretin is a hormone secreted into blood circulation by the intestines, and it stimulates the production of peptic juices in the pancreas when we have meals. In our research, we discovered secretin receptors in the brown adipose tissue of healthy people, which suggested that secretin also affects brown fat. Secretin infusions not only increased glucose uptake in brown adipose tissue, but also elevated energy expenditure in the whole body, says Doctoral Candidate, Cardiologist Sanna Laurila from the University of Turku.
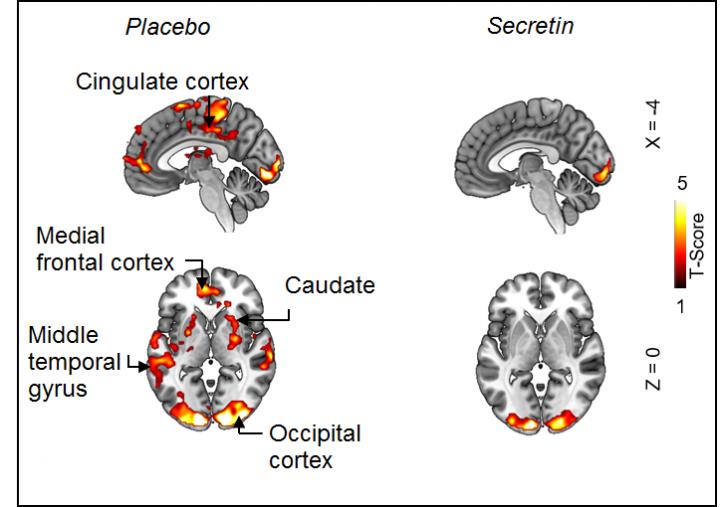
Using magnetic resonance imaging, the researchers discovered that secretin also decreased the activity of the reward system in the brain when the subjects were looking at delicious photos of food. The subjects’ decreased appetite could also be verified with a questionnaire survey, and the time between their meals grew by 40 minutes.
Brown fat generates great interest from the perspective of weight control because it has the ability to burn fat instead to storing it. However, humans have a relatively small amount of brown fat, which means that the metabolic advantages probably cannot be solely ascribed to increased energy consumption.
– This newly-confirmed message chain affecting satiation in people can be one of the reasons behind the beneficial metabolic effects of brown fat, sums Professor Pirjo Nuutila.
– This study underlines the functional relevance of human brown fat in controlling energy balance as it affects both food intake and energy expenditure, comments Professor Martin Klingenspor from the Technical University of Munich.
The newly-discovered mechanism controlling satiation opens up new opportunities for the research of the development, prevention, and treatment of obesity. Further research is needed to investigate in more detail what kind of role secretin has in metabolic disorders such as metabolic syndrome, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
###
In 2018, researchers from the Technical University of Munich and the Turku PET Centre discovered using mouse models a new mechanism mediated via brown adipose tissue and impacting satiation, and the research results were published in the journal Cell: https:/
Pirjo Nuutila’s research group is part of the InFLAMES Flagship which is a joint initiative of University of Turku and Åbo Akademi University. The goal of the Flagship is to integrate immunological and immunology-related research activities to develop and exploit new diagnostic and therapeutic tools. https:/
Media Contact
Pirjo Nuutila
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.