So-called quantum dots are a new class of materials with many applications. Quantum dots are realized by tiny semiconductor crystals with dimensions in the nanometre range. The optical and electrical properties can be controlled through the size of these crystals. As QLEDs, they are already on the market in the latest generations of TV flat screens, where they ensure particularly brilliant and high-resolution colour reproduction. However, quantum dots are not only used as “dyes”, they are also used in solar cells or as semiconductor devices, right up to computational building blocks, the qubits, of a quantum computer.
Now, a team led by Dr. Annika Bande at HZB has extended the understanding of the interaction between several quantum dots with an atomistic view in a theoretical publication.
Annika Bande heads the “Theory of Electron Dynamics and Spectroscopy” group at HZB and is particularly interested in the origins of quantum physical phenomena. Although quantum dots are extremely tiny nanocrystals, they consist of thousands of atoms with, in turn, multiples of electrons. Even with supercomputers, the electronic structure of such a semiconductor crystal could hardly be calculated, emphasises the theoretical chemist, who recently completed her habilitation at Freie Universität. “But we are developing methods that describe the problem approximately,” Bande explains. “In this case, we worked with scaled-down quantum dot versions of only about a hundred atoms, which nonetheless feature the characteristic properties of real nanocrystals.”
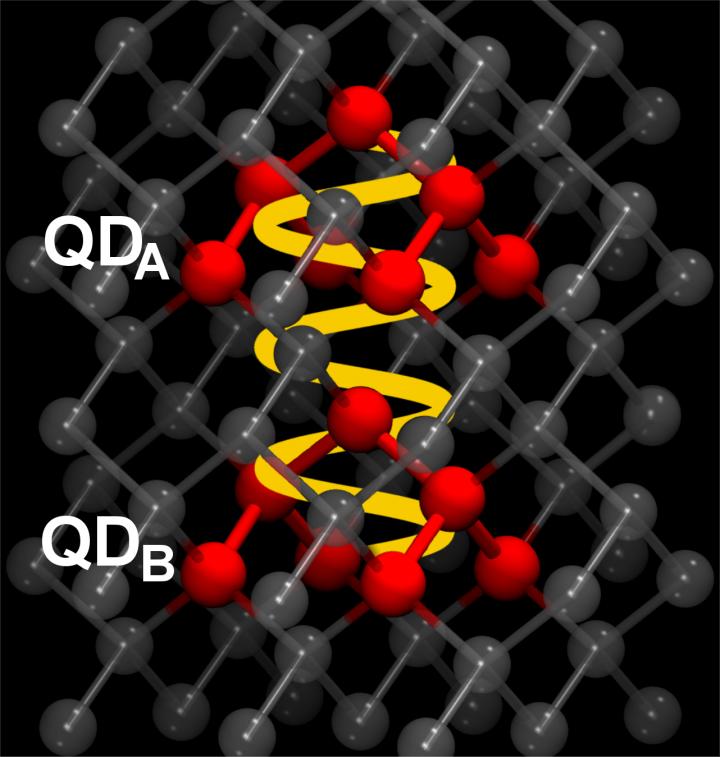
With this approach, after a year and a half of development and in collaboration with Prof. Jean Christophe Tremblay from the CNRS-Université de Lorraine in Metz, we succeeded in simulating the interaction of two quantum dots, each made of hundreds of atoms, which exchange energy with each other. Specifically, we have investigated how these two quantum dots can absorb, exchange and permanently store the energy controlled by light. A first light pulse is used for excitation, while the second light pulse induces the storage.
In total, we investigated three different pairs of quantum dots to capture the effect of size and geometry. We calculated the electronic structure with highest precision and simulated the electronic motion in real time at femtosecond resolution (10-15 s).
The results are also very useful for experimental research and development in many fields of application, for example for the development of qubits or to support photocatalysis, to produce green hydrogen gas by sunlight. “We are constantly working on extending our models towards even more realistic descriptions of quantum dots,” says Bande, “e.g. to capture the influence of temperature and environment.”
###
Pascal Krause / First Author of the publication
Media Contact
Antonia Roetger
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.