Contributing to embryogenesis and pathogenesis through long-term in vivo molecular imaging
A research group led by Takashi Saito, of the Ehime University Graduate School of Medicine, developed a 2-photon excitation light-sheet fluorescence microscope which (1) lowers phototoxicity, (2) extends the field of view, and (3) heightens spatial resolution. This microscope, when used for the observation of medaka fish, made it possible to observe the whole body of the embryo (an extended field of view) at a cellular level resolution (high spatial resolution) without affecting the growth of the fish (low phototoxicity) over a three-day span of embryonic development. This result was published in the scientific journal Nature Communications (Springer Nature).
1. Background
The fluorescence microscope is widely used in the field of life science to observe molecules inside a cell in a non-invasive way. Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy makes it possible to record three-dimensional images with high acquisition speed and high spatial resolution. However, in conventional light-sheet microscopes, it is difficult to limit photodamage to living tissues, and also difficult to simultaneously achieve wide FOV and high (cell level) spatial resolution.
2. Development of a two-photon excitation wide-field, light-sheet microscope
The Ehime University research group of Takashi Saitou, Sota Takanezawa, and Takeshi Imamura utilized the two-photon excitation phenomenon as a key to solving this problem. The two-photon excitation microscope with infrared lasers enables gentle (low phototoxic) imaging of living organisms. However, because the light must be focused on a narrow range to induce two-photon excitation, the excitation range (in light-sheet microscope, the field of view) is narrow. In order to solve this, we developed simple illumination optics unit with a Bessel beam that expands the laser propagation range in the direction of the optic axis (Fig. 1A). This unit can stretch the beam length to 600-1000 μm while maintaining a 2-3 μm axial resolution when using a 10x magnification NA0.3 objective lens. Using this optical unit, we constructed a two-photon excitation light-sheet microscopy (Fig. 1B), which makes it possible to perform whole-body imaging of medaka larvae with cellular resolution (Fig. 1C).
3. Application to live imaging
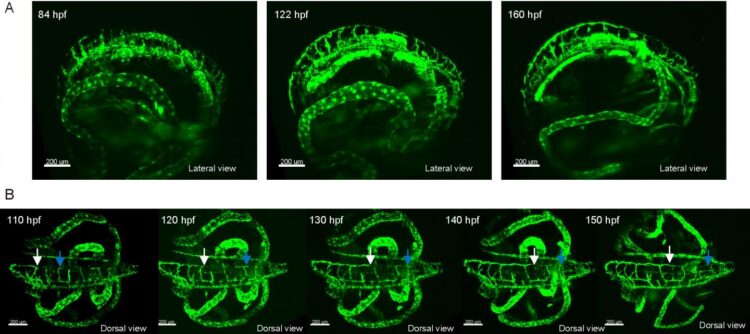
The medaka is widely used as a model organism for vertebrate. It is suitable for fluorescent imaging since it is small and transparent. To evaluate the applicability of our microscope for use on living organisms, we performed a phototoxicity assessment. This revealed reduced photodamage compared with the conventional Gaussian beam light-sheet sheet microscope. It is therefore suggested to be suitable for long-term live imaging. We then applied long-term time-lapse imaging of the transgenic medaka in which lymphatic endothelium is labelled with green fluorescent protein, and succeeded in live imaging over three days at intervals of 5 minutes (Fig. 2).
4. Significance of the research
In this study, we developed a new high performance light-sheet fluorescence microscope. Using this technology, we can observe almost all the embryonic growth processes of medaka fish with high cellular resolution over the whole body of the fish. This technology is expected to contribute to the molecular level understanding of embryonic development, the elucidation of pathogenesis for lifestyle-related diseases, and to further the technology of drug development.
###
Media Contact
Public Relations Division
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.