Radio telescope images enable a new way to study magnetic fields in galaxy clusters millions of light years away
Credit: Modified from Chibueze, Sakemi, Ohmura et al. (2021) Nature Fig. 1(b)
For the first time, researchers have observed plasma jets interacting with magnetic fields in a massive galaxy cluster 600 million light years away, thanks to the help of radio telescopes and supercomputer simulations. The findings, published in the journal Nature, can help clarify how such galaxy clusters evolve.
Galaxy clusters can contain up to thousands of galaxies bound together by gravity. Abell 3376 is a huge cluster forming as a result of a violent collision between two sub-clusters of galaxies. Very little is known about the magnetic fields that exist within this and similar galaxy clusters.
“It is generally difficult to directly examine the structure of intracluster magnetic fields,” says Nagoya University astrophysicist Tsutomu Takeuchi, who was involved in the research. “Our results clearly demonstrate how long-wavelength radio observations can help explore this interaction.”
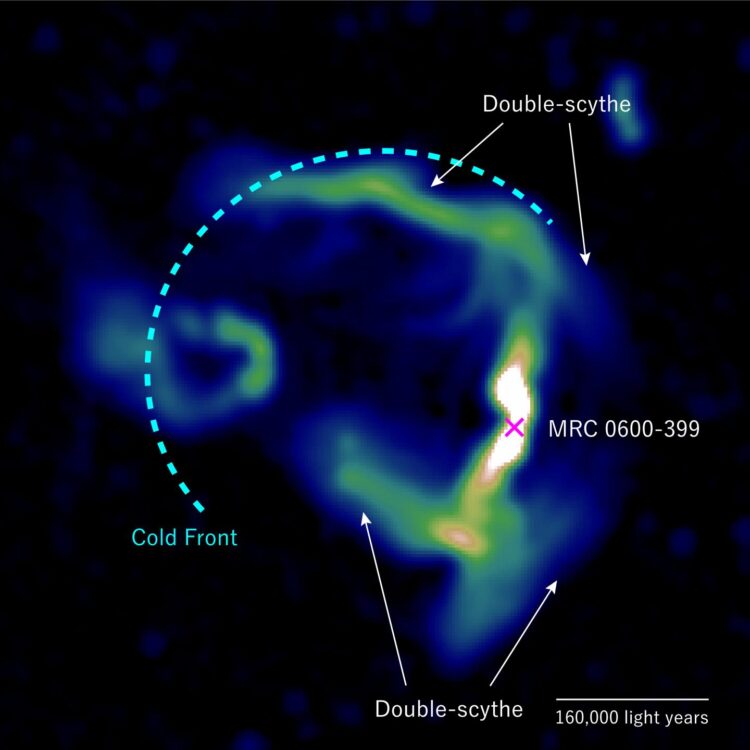
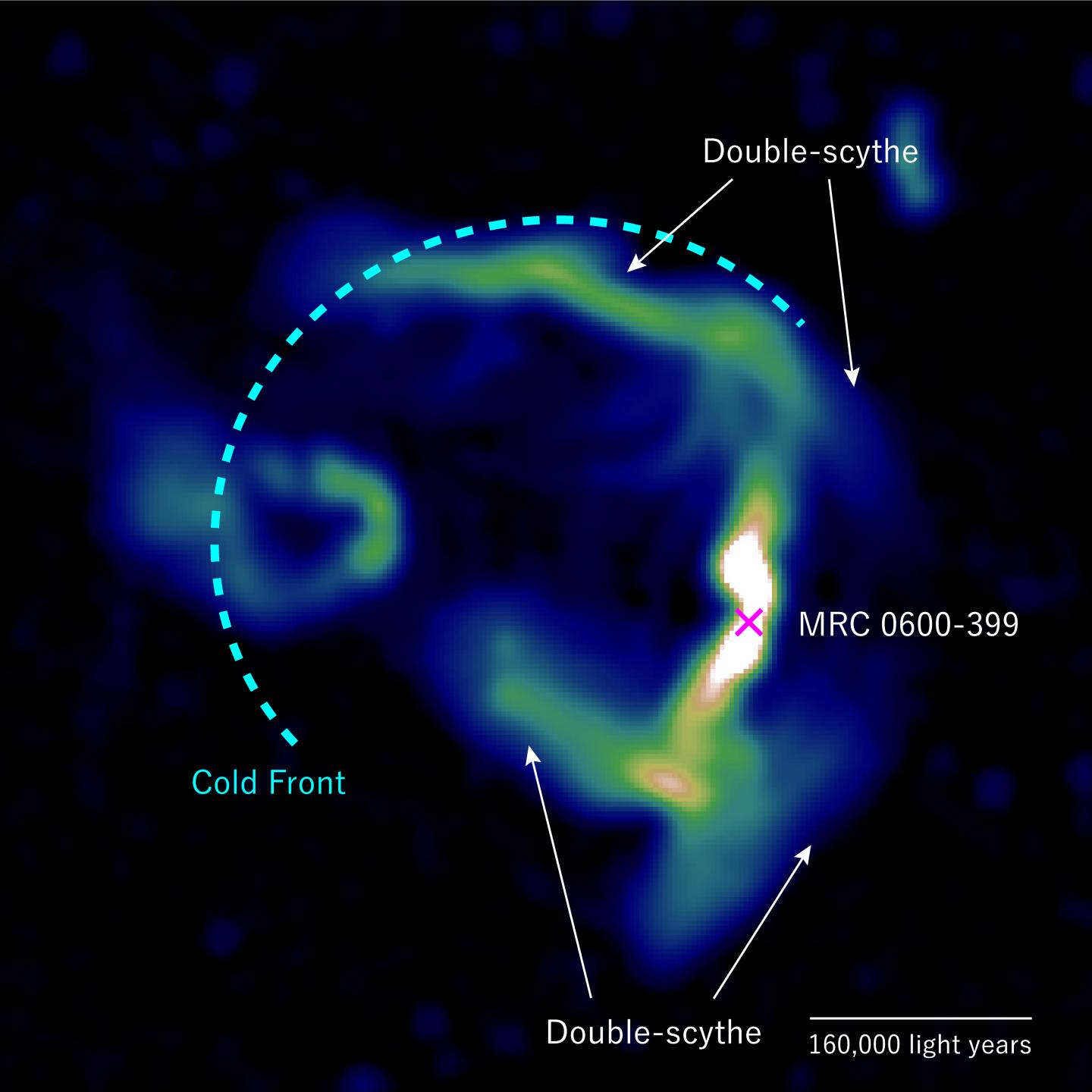
An international team of scientists have been using the MeerKAT radio telescope in the Northern Cape of South Africa to learn more about Abell 3376’s huge magnetic fields. One of the telescope’s very high-resolution images revealed something unexpected: plasma jets emitted by a supermassive black hole in the cluster bend to form a unique T-shape as they extend outwards for distances as far as 326,156 light years away. The black hole is in galaxy MRC 0600-399, which is near the centre of Abell 3376.
The team combined their MeerKAT radio telescope data with X-ray data from the European Space Agency’s space telescope XXM-Newton to find that the plasma jet bend occurs at the boundary of the subcluster in which MRC 0600-399 exists.
“This told us that the plasma jets from MRC 0600-399 were interacting with something in the heated gas, called the intracluster medium, that exists between the galaxies within Abell 3376,” explains Takeuchi.
To figure out what was happening, the team conducted 3D ‘magnetohydrodynamic’ simulations using the world’s most powerful supercomputer in the field of astronomical calculations, ATERUI II, located at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan.
The simulations showed that the jet streams emitted by MRC 0600-399’s black hole eventually reach and interact with magnetic fields at the border of the galaxy subcluster. The jet stream compresses the magnetic field lines and moves along them, forming the characteristic T-shape.
“This is the first discovery of an interaction between cluster galaxy plasma jets and intracluster magnetic fields,” says Takeuchi.
An international team has just begun construction of what is planned to be the world’s largest radio telescope, called the Square Kilometre Array (SKA).
“New facilities like the SKA are expected to reveal the roles and origins of cosmic magnetism and even to help us understand how the universe evolved,” says Takeuchi. “Our study is a good example of the power of radio observation, one of the last frontiers in astronomy.”
###
The study, “Jets from MRC 0600-399 bent by magnetic fields in the cluster Abell 3376,” was published in the journal Nature on May 5, 2021, at https:/
About Nagoya University, Japan
Nagoya University has a history of about 150 years, with its roots in a temporary medical school and hospital established in 1871, and was formally instituted as the last Imperial University of Japan in 1939. Although modest in size compared to the largest universities in Japan, Nagoya University has been pursuing excellence since its founding. Six of the 18 Japanese Nobel Prize-winners since 2000 did all or part of their Nobel Prize-winning work at Nagoya University: four in Physics – Toshihide Maskawa and Makoto Kobayashi in 2008, and Isamu Akasaki and Hiroshi Amano in 2014; and two in Chemistry – Ryoji Noyori in 2001 and Osamu Shimomura in 2008. In mathematics, Shigefumi Mori did his Fields Medal-winning work at the University. A number of other important discoveries have also been made at the University, including the Okazaki DNA Fragments by Reiji and Tsuneko Okazaki in the 1960s; and depletion forces by Sho Asakura and Fumio Oosawa in 1954.
Website: http://en.
Media Contact
Tsutomu T. Takeuchi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.