Credit: The authors
Image fusion is a process that can enhance the clinical value of medical images, improving the accuracy of medical diagnoses and the quality of patient care.
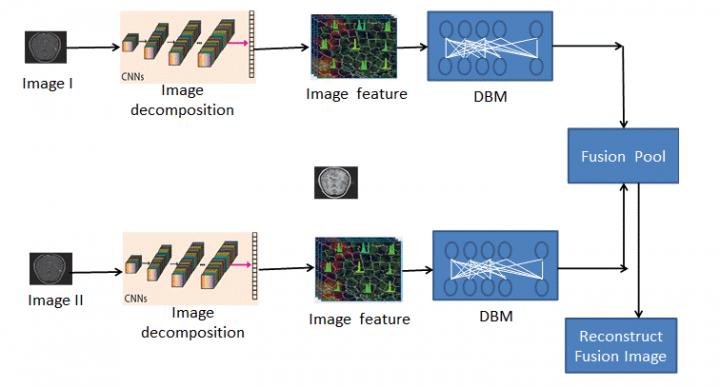
Researchers at the College of Data Science Software Engineering at China’s Qingdao University, have developed a new ‘multi-modal’ image fusion method based on supervised deep learning that enhances image clarity, reduces redundant image features and supports batch processing. Their findings have just been published in KeAi’s International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering.
Author Yi Li explains: “Most medical images have unilateral or limited information content; for instance, focus positions vary which can make some objects appear blurred. Having important information scattered across a number of images can hamper a doctor’s judgment. Image fusion is an effective solution – it automatically detects the information contained in those separate images and integrates them to produce one composite image.”
Researchers are increasingly turning to deep learning to improve image fusion. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, draws on artificial neural networks that are designed to imitate how humans think and learn. That means it is capable of learning from data that is unstructured or unlabelled.
However much of the current research focuses on the application of deep learning in single image fusion processing. Studies that use it for multi-image batch processing are much rarer.
Li explains: “Medical images have specific practical requirements, including information richness and high clarity. During our study, we used successful image fusion results to build an image-training database. We were then able to use that database to fuse medical images in batches.”
Li adds: “Our method also enhances the clarity of MRI, CT and SPECT image fusion, improving the accuracy of medical diagnosis. We have achieved state-of the-art performance in terms of both visual quality and quantitative evaluation metrics. For example, the fused images we produced look more natural, and have sharper edges and higher resolution. In addition, detailed information and features of interest are better preserved.”
###
Contact the paper’s author: Yi Li, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Media Contact
Cassie He
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




