Credit: The authors
Extracting hydrogen from water through electrolysis offers a promising route for increasing the production of hydrogen, a clean and environmentally friendly fuel. But one major challenge of water electrolysis is the sluggish reaction of oxygen at the anode, known as the oxygen evolution reaction (OER).
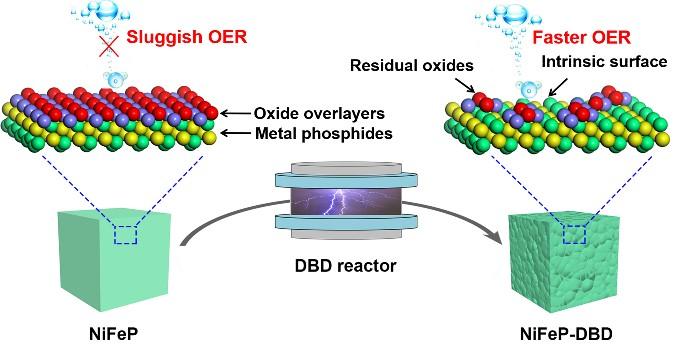
A collaboration between researchers at Hunan University and Shenzhen University in China, has led to a discovery that promises to improve the OER process. In their recent paper, published in the KeAi journal Green Energy & Environment, they report that etching – or, in other words, chemically removing – the oxide overlayers that form on the surface of the metal phosphide electrocatalysts regularly used in electrolysis, can increase OER efficiency.
Professor Shuangyin Wang of the State Key Laboratory of Chem/Bio-sensing and Chemometrics at Hunan University led the study. He explains: “While metal phosphides are often used as catalysts due to their unique physicochemical properties such as high conductivity, earth-abundance reserves and excellent performance, a common, but often neglected fact is that they are quick to suffer atmospheric oxidation when they are exposed to air. This causes them to form oxide overlayers on their surface, which can change the surface reconstruction process and confuse the structure-performance relationship.”
To solve this problem, Professor Wang and his colleagues decided to etch away those oxide overlayers using a dielectric barrier discharge plasma technique. And they discovered that the etching process not only accelerated the surface reconstruction process, but greatly enhanced the formation of metal hydroxides and OER activity.
According to Prof. Wang: “These findings are helpful for understanding the structure-performance relationship of metal phosphides in electrooxidation reaction. And we suspect that the same etching process has the potential to be used on other oxygen-susceptible metal compounds such as chalcogenides, nitrides and carbides.
“Our hope is that our study guides the rational design and engineering of more efficient electrocatalysts for water electrolysis.”
###
Contact the paper’s lead author: Shuangyin Wang, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Media Contact
Cassie He
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




