Credit: POSTECH
The skin, which covers the surface of the human body, is its largest organ. It is the first organ to show changes stemming from organ or physiological activity. It is especially common for diabetic patients to suffer from skin diseases or infections. Recently, a POSTECH research team has succeeded in creating a 3D artificial skin that enables observation of skin diseases of diabetic patients.
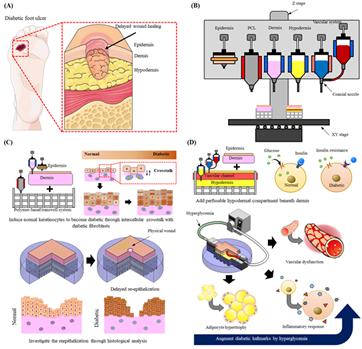
A research team led by Professor Dong-Woo Cho and Minjun Ahn of POSTECH’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Byoung Soo Kim of School of Biomedical Convergence Engineering at Pusan National University has successfully produced an in vitro diseased skin model that displays the pathophysiological hallmarks of type 2 diabetes based on 3D cell printing system. These research findings were recently published in Biomaterials, a world-renowned international journal in biomaterials.
Despite continuous research to produce artificial skin with 3D cell printing technology, artificial skin displaying the pathological process present in the native skin has not been reported yet.
Inspired by the interaction between the epidermis and skin cells found in real skin, the research team hypothesized that when normal keratinocytes interact with the dermal layer made of diabetic fibroblasts, they will differentiate into diabetic epidermis. To prove this, diabetic artificial skin with skin wounds based on 3D printing technique was fabricated using each cell.
In this diabetic artificial skin, slow re-epithelialization, a typical feature of diabetic skin, was observed. In addition, when the diabetic fat tissue layer containing blood vessels was added, insulin resistance, adipocyte hypertrophy, pro-inflammatory response, and vascular dysfunction, which are commonly observed in diabetes, were confirmed.
“Through 3D cell printing, we can now observe skin diseases in vitro, without actually experiencing it,” remarked the researchers. “We anticipate it to be a way to replace animal models that have been conventionally used to observe skin diseases. It is significant that its applicability as a disease model for new drug development has been proven.”
###
This research was conducted with the support from the Creative Research Program and the Nano-New Materials Core Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Media Contact
Jinyoung Huh
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




