Credit: Tohoku University
Cells talk to each other to coordinate nutrition, waste removal, energy use, and, in some cases, disease progression. The cells that line the surfaces of organs or specific tissues, called epithelial cells, appear to speak two different languages – one for either side of the cell, according to a new study by researchers based in Japan.
The discovery, published on March 16 in EMBO Reports, could have implications for understanding how cancer spreads and, potentially, for advanced treatments, the team says.
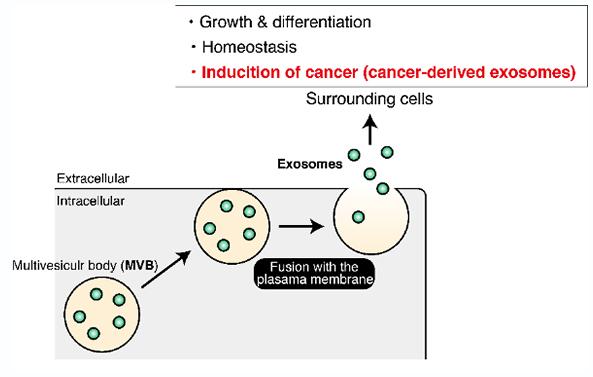
The team, led by Mitsunori Fukuda, professor in the Laboratory of Membrane Trafficking Mechanisms, Department of Integrative Life Sciences, Graduate School of Life Sciences at Tohoku University, examined epithelial cells from a kidney model. The cells release particles called exosomes that carry bits of the cells themselves or information about the cells. The proteins and other genetic information in the exosomes can then influence how other cells behave or function. In health, such an information exchange could help the immune system mount a more tailored approach to an invading pathogen. Some diseased cells, such as cancer, can release exosomes that make healthy cells less resistant to invasion.
“Single cells are known to release various kinds of exosomes, but very little is known about the mechanisms by which they are produced and released,” Fukuda said. “In this paper, we found that epithelial cells asymmetrically release two distinct types of exosomes with distinct protein compositions.”
The researchers developed a purification method to separate out exosomes based on their protein makeup.
“In this paper, we found that epithelial cells asymmetrically release two distinct types of exosomes – apical and basolateral – with distinct protein compositions,” said first author Takahide Matsui, assistant professor, Laboratory of Membrane Trafficking Mechanisms, Department of Integrative Life Sciences, Graduate School of Life Sciences at Tohoku University.
They found that exosomes released from the apical side of the cell, which faces an external space or lumen, were modulated by ALIX, a protein related to the particle formation inside the cells. Exosomes released from the basolateral side of the cell closest to other tissues and neighboring cells were triggered by ceramide, a fatty molecule. They also found that depleting ALIX and ceramide reduced the number of apical exosomes and basolateral exosomes released, respectively.
Fukuda said that the results could help elucidate the cell-to-cell communication that allows cancer to migrate – and put a stop to it.
“It will be interesting to investigate how cancer cells use two distinct mechanisms of exosome production during cancer progression,” Fukuda said. “Since exosomes from cancer cells are involved in their progression, our findings could lead to the discovery of new drugs for treatments for cancers in the future.”
Matsui agreed, noting that their research could expand to other realms in health and in disease.
“Our discovery provides an important clue to understanding the generation of different exosomes in many cell types in addition to epithelial cells,” Matsui said.
###
Media Contact
Mitsunori Fukuda
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




