Study aims to recruit 2,000 participants at high risk of developing HCC from 6 healthcare institutions and 8 polyclinics across Singapore
Credit: Image credit: Mole DJ et al. Plos One. 2020;15(12):e0238568
- Only 20% of primary liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are diagnosed at an early stage, which makes early detection an urgent, unmet healthcare need.
- Study aims to develop more accurate diagnostics for early HCC, an AI algorithm to predict an individual’s risk of developing HCC, and discover novel molecular targets to prevent the development of HCC.
- Study aims to recruit 2,000 participants at high risk of developing HCC from six healthcare institutions and eight polyclinics across Singapore.
Singapore, 3 May 2021 – A first of its kind cohort study on patients at high risk of developing primary liver cancer also known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), has been launched to diagnose HCC more accurately at an earlier stage and to predict an individual’s likelihood of developing the cancer. HCC is the sixth most common cancer in the world but the third most common cause of cancer deaths globally1. In Singapore, HCC is the third and fourth most common cause of cancer deaths, amongst males and females respectively2. While potentially curative treatment is possible with early diagnosis, only 20% of HCC cases are detected at a stage where cure is possible. This investigator-initiated multi-centre study led by the National Cancer Centre of Singapore (NCCS) called EarLy DEtection of HCC: miRNA, microbiome and imaGing biomArkers in the evolution of chroNiC livEr Disease in a high-risk prospective cohort (ELEGANCE), addresses this urgent, unmet need for individuals at high risk of developing HCC.
1. Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 68(6), 394-424. https:/
2. National Registry of Diseases Office. (2021, March).
Singapore Cancer Registry Annual Report 2018. https:/
While individuals at high risk of developing HCC are well defined clinically as those with pre-existing liver cirrhosis, chronic viral hepatitis and/or fatty liver, there are currently no validated diagnostic, predictive and prognostic biomarkers for HCC, making early diagnosis challenging. Identifying such biomarkers would greatly improve patient outcomes. Currently, emerging data suggest that the evolution of chronic liver disease into HCC may be reflected by changes in the stool (microbiome), blood and urine (metabolome). An AI algorithm that leverages MRI imaging parameters may also be able to predict an individual’s risk of developing HCC by offering personalised prediction.
The ELEGANCE study will enrol patients at high-risk of developing HCC to deliver robust scientific data with the aim of developing more precise clinical tools to diagnose HCC at an early stage and predict which individuals are at highest risk. In addition, the study will highlight how the microbiome and metabolome changes with disease development and identify potential therapeutic targets that may slow disease progression and reduce the risks of developing cancer.
“Having cared for patients with liver cancer for more than 20 years, I see a pressing need to better predict this disease, diagnose it early and improve treatment outcomes,” said Prof Pierce Chow, Principal Investigator of the study and Senior Consultant, Division of Surgery and Surgical Oncology, Singapore General Hospital (SGH) and NCCS. “The ELEGANCE study is the first in the world to prospectively investigate the role of microRNA (miRNA), microbiome, metabolome and imaging biomarkers in the evolution of chronic liver disease and the early diagnosis of liver cancer.”
“This landmark study is designed to provide in-depth and multi-faceted data on the prognosis of HCC which can offer important insights to developing potential new diagnostic and predictive tools for this cancer,” said Assistant Professor Mihir Gandhi, Health Services & Systems Research Signature Programme and Head of Biostatistics Core team at the Centre for Quantitative Medicine, Duke-NUS Medical School (Duke-NUS), Singapore, whose team shaped the study design. “Data and analysis from this study will provide a robust scientific basis for the development of prognostic models that can identify those at risk of developing HCC and other unfavourable outcomes.”
“Metabolites can be used as early indicators of health problems on the horizon. We will perform metabolic phenotyping of the cohort at high risk of developing HCC, and we should be able to identify early biomarkers that can predict the onset of HCC. The outcome could provide clues for regulating gut microbes by precision nutritional intervention to slow down or prevent the development of HCC,” said Prof Wang Yulan, Director of the Singapore Phenome Centre (SPC) at Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University Singapore.
Conducting the ELEGANCE study in Singapore
With 80% of HCC cases worldwide diagnosed in the Asia Pacific region, Singapore is a fitting site to conduct the study.3 The four-year long study launched late last month will enroll 2,000 participants at risk for HCC. These include patients with liver cirrhosis, hepatitis B or C, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
The study involves public and private sector collaboration and has three tracks: 1) to evaluate the efficacy of a miRNA diagnostic kit for HCC with Singapore-headquartered multi-cancer early detection company MiRXES; 2) to develop an AI algorithm for identification of patients at-risk of developing HCC using state-of-the-art quantitative MR imaging, with digital medical technology company, Perspectum, whose Asia Pacific headquarters are in Singapore; and 3) to determine the changes in the microbiome and metabolome that lead to HCC with Southeast Asian precision gut microbiome company AMiLi.
The goal of all three tracks is early diagnosis, better and more cost effective methods for improved patient outcomes and the identification of novel therapeutic targets.
3. National Registry of Diseases Office. (2019, November). Singapore Cancer Registry 50th Anniversary Monograph – Appendices. https:/
Whole-of nation effort
Healthcare institutions including National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), Singapore General Hospital (SGH), National University Hospital (NUH), Changi General Hospital (CGH), Sengkang General Hospital (SKH), Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH) and eight SingHealth Polyclinics (Bedok, Bukit Merah, Marine Parade, Outram, Pasir Ris, Punggol, Sengkang and Tampines) will serve as recruitment sites. Clinician-scientists and scientists from the recruiting hospitals and polyclinics, as well as academic institutions, Duke-NUS and Singapore Phenome Centre are collaborators for this study.
“There is indeed a pressing need for a collaborative multi-center study to identify patients at the highest risk of HCC in Singapore. In the era of precision medicine, we aim to develop state-of-the-art diagnostic tools to effectively diagnose HCC at an early stage. Our common goal is to reduce mortality from HCC,” said Associate Professor Jason Chang Pik Eu, Head and Senior Consultant, Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, SGH.
Associate Professor Dan Yock Young, Senior Consultant, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, NUH said, “Liver cancer is one of the deadliest cancers in Asia. Developing new tools of screening and identification of the at risk population will allow us to detect cancer at its earlier stage, where it is potentially curative.”
This study is supported by a SGD10 million grant from the Agency of Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) as well as cash and in-kind contribution of more than SGD15 million from the three industry partners.
Patient recruitment for the ELEGANCE study
The research team is actively recruiting patients with chronic liver disease as validated by blood tests and imaging. Enrolled patients will be monitored regularly by current standard-of-care imaging and blood tests. Collection of additional clinical data, bio samples and regular follow-ups will continue at participating hospitals/clinics for up to three years after enrolment. As this is an observational research study, there will be no interventional treatment but patients diagnosed with liver cancer during the study will be treated by the respective healthcare institutions according to standard clinical practice.
###
For more information on the study and eligibility, please contact the study’s coordinators:
Tel: +65 6326 6573
Email: [email protected]
Accompanying image
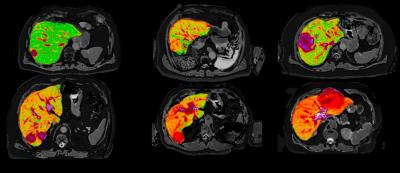
Caption: Quantitative MR images of the liver from six patients presenting with liver cancer produced by Perspectum’s LiverMultiScan which will be used in a new study led by National Cancer Centre Singapore.
Image credit: Mole DJ et al. Plos One. 2020;15(12):e0238568
About the National Cancer Centre of Singapore
The National Cancer Centre of Singapore (NCCS) provides a holistic and multi-disciplinary approach to cancer treatment and patient care. We see close to 65 per cent of the public sector oncology cases, and they are benefiting from the sub-specialisation of our clinical oncologists.
To deliver among the best in cancer treatment and care, our clinicians work closely with our scientists who conduct robust, cutting-edge clinical and translational research programmes which are internationally recognised. NCCS strives to be a global leading cancer centre, and shares its expertise and knowledge by offering training to local and overseas medical professionals.
For more information, please visit: http://www.
About Duke-NUS Medical School
Duke-NUS is Singapore’s flagship graduate entry medical school, established in 2005 with a strategic, government-led partnership between two world-class institutions: Duke University School of Medicine and the National University of Singapore (NUS). Through an innovative curriculum, students at Duke-NUS are nurtured to become multi-faceted ‘Clinicians Plus’ poised to steer the healthcare and biomedical ecosystem in Singapore and beyond. A leader in ground-breaking research and translational innovation, Duke-NUS has gained international renown through its five signature research programmes and nine centres. The enduring impact of its discoveries is amplified by its successful Academic Medicine partnership with Singapore Health Services (SingHealth), Singapore’s largest healthcare group. This strategic alliance has spawned 15 Academic Clinical Programmes, which harness multi-disciplinary research and education to transform medicine and improve lives.
For more information, please visit http://www.
About Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
A research-intensive public university, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has 33,000 undergraduate and postgraduate students in the Engineering, Business, Science, Humanities, Arts, & Social Sciences, and Graduate colleges. It also has a medical school, the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, set up jointly with Imperial College London.
NTU is also home to world-class autonomous institutes – the National Institute of Education, S Rajaratnam School of International Studies, Earth Observatory of Singapore, and Singapore Centre for Environmental Life Sciences Engineering – and various leading research centres such as the Nanyang Environment & Water Research Institute (NEWRI) and Energy Research Institute @ NTU (ERI@N).
Ranked amongst the world’s top universities by QS, NTU has also been named the world’s top young university for the past seven years. The University’s main campus is frequently listed among the Top 15 most beautiful university campuses in the world and it has 57 Green Mark-certified (equivalent to LEED-certified) building projects, of which 95% are certified Green Mark Platinum. Apart from its main campus, NTU also has a campus in Singapore’s healthcare district.
Under the NTU Smart Campus vision, the University harnesses the power of digital technology and tech-enabled solutions to support better learning and living experiences, the discovery of new knowledge, and the sustainability of resources.
For more information, visit our website.
For more information, please contact:
National Cancer Centre Singapore
Dharshini Subbiah
Assistant Manager, Corporate Communications
Mobile : 9616 7532
Email : [email protected]
Duke-NUS Medical School
Yu Zehan
Senior Media Specialist, Communications & Strategic Relations
Mobile : 9839 6957
Email : [email protected]
Singapore Phenome Centre, Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University Singapore
Shireen Federico
Manager, Publications, Communications and Outreach
Office : 6592 3873
Email : [email protected]
Media Contact
Dharshini Subbiah
[email protected]




