Team of physicists led by Professor Frank Cichos develop learning microswimmers
Credit: Photo: Leipzig University, Faculty of Physics and Earth Sciences
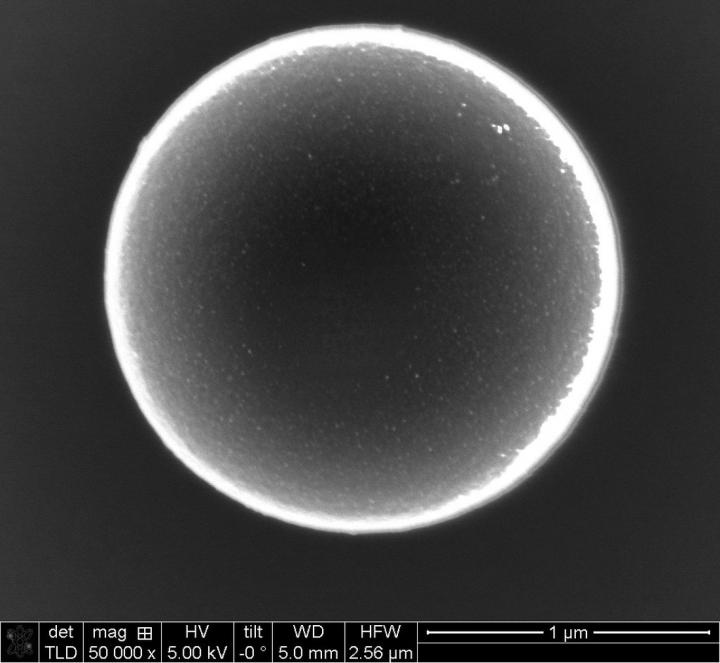
Microswimmers are artificial, self-propelled, microscopic particles. They are capable of directional motion in a solution. The Molecular Nanophotonics Group at Leipzig University has developed special particles that are smaller than one-thirtieth of the diameter of a hair. They can change their direction of motion by heating tiny gold particles on their surface and converting this energy into motion. “However, these miniaturised machines cannot take in and learn information like their living counterparts. To achieve this, we control the microswimmers externally so that they learn to navigate in a virtual environment through what is known as reinforcement learning,” said Cichos.
With the help of virtual rewards, the microswimmers find their way through the liquid while repeatedly being thrown off of their path, mainly by Brownian motion. “Our results show that the best swimmer is not the one that is fastest, but rather that there is an optimal speed,” said Viktor Holubec, who worked on the project as a fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and has now returned to the university in Prague. According to the scientists, linking artificial intelligence and active systems like in these microswimmers is a first small step towards new intelligent microscopic materials that can autonomously perform tasks while also adapting to their new environment. At the same time, they hope that the combination of artificial microswimmers and machine learning methods will provide new insights into the emergence of collective behaviour in biological systems. “Our goal is to develop artificial, smart building blocks that can perceive their environmental influences and actively react to them,” said the physicist. Once this method is fully developed and has been applied to other material systems, including biological ones, it could be used, for example, in the development of smart drugs or microscopic robot swarms.
###
Original title of the publication in Science Robotics:
“Reinforcement Learning with Artificial Microswimmers”
Media Contact
Professor Frank Cichos
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




