Credit: ©?Scientific Reports
Point
Epithelial cell rests of Malassez derived from the periodontal ligament were transformed into progenitor stem-like cells by stimulation with epigenetic agents.
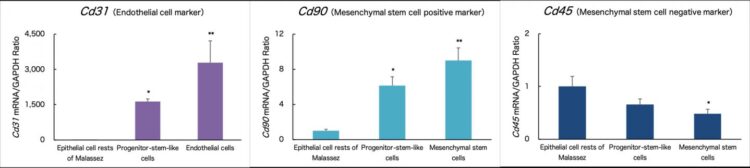
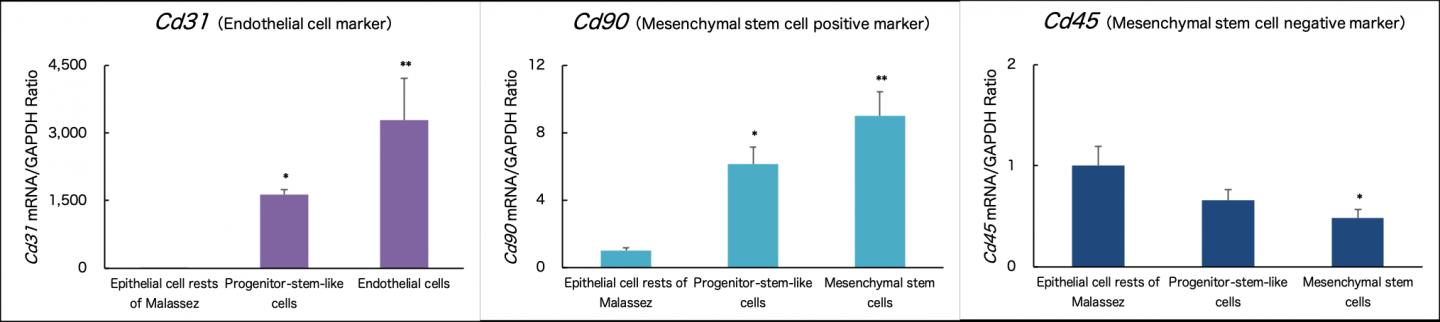
Subsequently, the progenitor stem-like cells were directly differentiated into endothelial, mesenchymal stem, and osteogenic cells that constitute the periodontal ligament.
Background
Stem cells derived from the dental pulp or periodontal ligament have been used for regenerative dentistry. Although it is relatively easy to collect the dental pulp stem cells, it is difficult to obtain adequate numbers of good quality cells; a stable supply is required for their application in regenerative dentistry. In the present study, we generated the progenitor-stem-like cells from ERM cells in the periodontal ligament using the epigenetic modifications without gene transfer. The progenitor stem-like cells were differentiated into endothelial, mesenchymal stem, and osteogenic cells–which constitute the periodontal ligament–using a direct reprogramming method that induces the differentiation of progenitor stem cells into the target cells.
Methods and Results
The isolated ERM cells were induced to differentiate into progenitor stem-like cells, which were similar to stem cells, following stimulation with the epigenetic agents, 5-Azacytidine and Valproic acid, for 1 week. The progenitor stem-like cells expressed the protein stem cell markers NANOG and OCT3/4, which were also observed in the iPS cells (Figure 1).
The progenitor stem-like cells were differentiated into endothelial, mesenchymal stem, and osteogenic cells. The expression of the specific marker for each cell type was confirmed (Figures 2 and 3).
Future prospects
The findings of the present study may contribute to the development of new periodontal regenerative therapy. Epigenetic agents have been successfully applied in various human diseases, including cancers. Nonetheless, further investigations are needed to confirm the findings of this study.
###
Research grants
This research was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Early-Career Scientists from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (No. 18K17091).
Press information
Press; Scientific Reports
Title; Direct reprogramming of epithelial cell rests of malassez into mesenchymal-like cells by epigenetic agents
Authors; Koki Yoshida, Osamu Uehara, Yoshihito Kurashige, Durga Paudel, Aya Onishi, Puja Neopane, Daichi Hiraki, Tetsuro Morikawa, Fumiya Harada, Rie Takai, Jun Sato, Masato Saitoh, Yoshihiro Abiko*. (*; Corresponding author)
Online publication date and Embargo; 20th January 2021 at 10 am (UK time).
DOI; 10.1038/s41598-020-79426-4
Contact
About research
Yoshihiro Abiko, BA, DDS., Ph.D., Division of Oral Medicine and Pathology, Department of Human Biology and Pathophysiology, School of Dentistry, Health Sciences University of Hokkaido, 1757 Kanazawa, Ishikari-Tobetsu, Hokkaido, 061-0293, Japan
Tel. +81-133-23-1390 ; Fax. +81-133-23-1390 : e-mail: [email protected]
Public relations
International Education and Exchange Center, Health Sciences University of Hokkaido, 1757 Kanazawa, Ishikari-Tobetsu, Hokkaido, 061-0293, Japan
Tel. +81-133-23-1211 : e-mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
Yoshihiro Abiko
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.