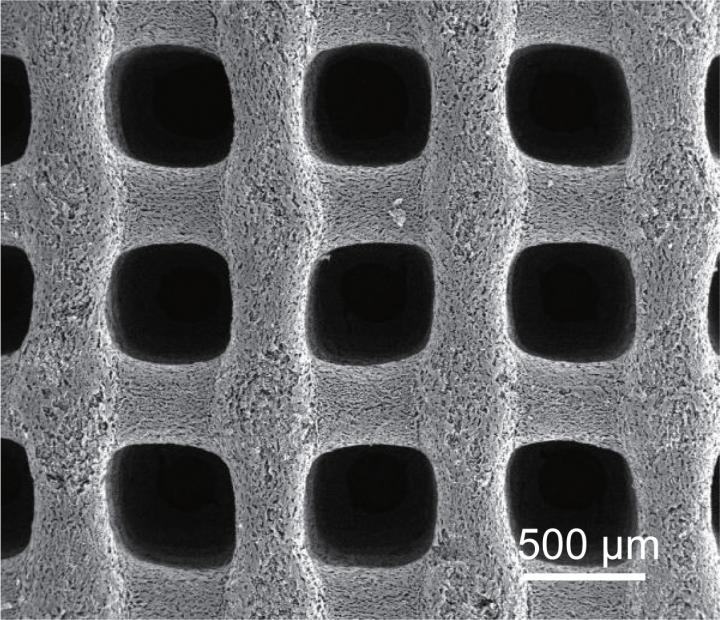
Credit: Adapted from Nano Letters 2021, DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04780
NASA’s Perseverance Rover recently made a successful landing on Mars, embarking on a two-year mission to seek signs of ancient life and collect samples. Because Mars is extremely cold — nighttime temperatures can drop below -112 F — heaters are required to keep the rover’s battery system from freezing. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters have 3D printed porous carbon aerogels for electrodes in ultralow-temperature supercapacitors, reducing heating needs for future space and polar missions.
Jennifer Lu, Yat Li and colleagues wanted to develop an energy storage system that could operate at very low temperatures without heating units, which add weight and energy requirements to instruments and machinery, such as the Mars rovers. So the researchers 3D printed a porous carbon aerogel using cellulose nanocrystal-based ink, and then freeze-dried it and further treated the surface. The resulting material had multiple levels of pores, from the 500-μm pores in the lattice-like structure, to nanometer-sized pores within the bars of the lattice. This multiscale porous network preserved adequate ion diffusion and charge transfer through an electrode at -94 F, achieving higher energy storage capacitance than previously reported low-temperature supercapacitors. The team will collaborate with NASA scientists to further characterize the device’s low-temperature performance.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the Merced nAnomaterials Center for Energy and Sensing, NASA, the University of California, Santa Cruz and the U.S. Department of Energy.
The paper’s abstract will be available on March 10 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.
For more of the latest research news, register for our upcoming meeting, ACS Spring 2021.
Journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration by emailing us at [email protected].
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us:
Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]




