Credit: Hao Li
Peer review/Experimental study/Cells
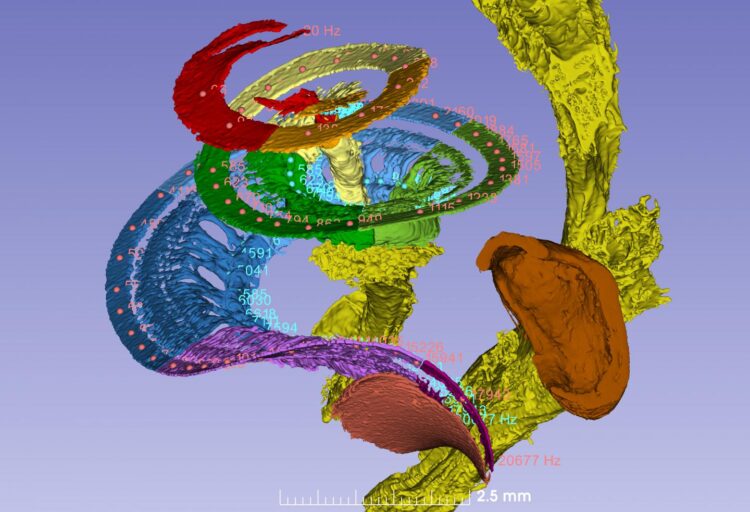
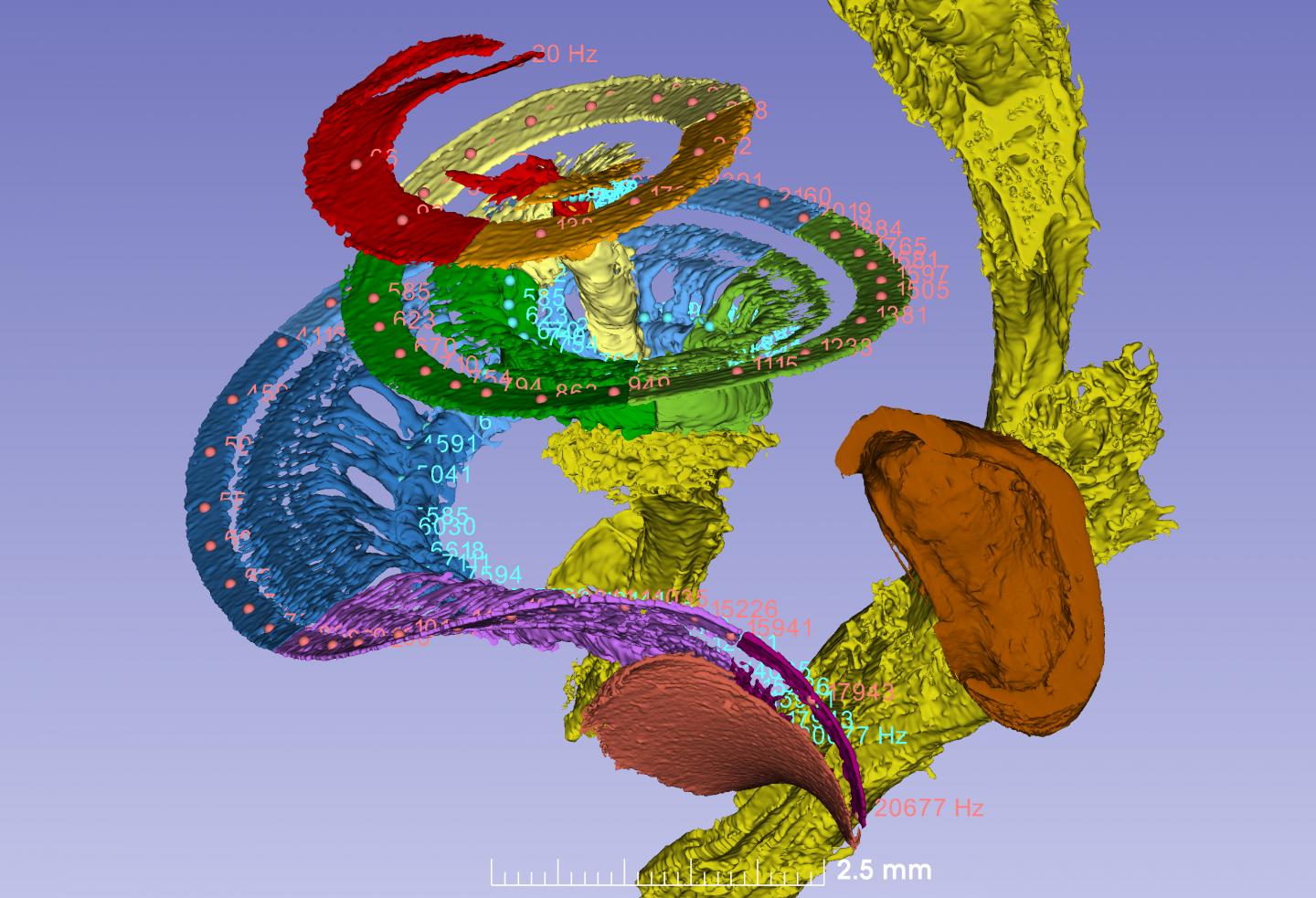
Researchers at Uppsala University have created the first 3D map of the hearing nerve showing where the various sound frequencies are captured. Using what is known as synchrotron X-ray imaging, they were able to trace the fine nerve threads and the vibrating auditory organ, the cochlea, and find out exactly how the frequencies of incoming sound are distributed. The study is published in Scientific Reports.
“This can make treatment with cochlea implants for the hearing-impaired more effective,” says Helge Rask-Andersen, Professor of Experimental Otology at Uppsala University.
Sound waves have differing frequencies – that is, the number of vibrations they make every second varies according to whether it is a high-pitched sound, which causes more vibrations per second, or a low-pitched one, which results in fewer. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz), and the human ear can perceive frequencies of between 20 and 20,000 Hz.
When the sound waves are captured by the cochlea of the inner ear, fibrous connective tissue and sensory cells separate the various frequencies. High-frequency sounds reach the sound-sensitive hair cells in the lower part of the cochlea, while low-frequency sounds are absorbed in the corresponding way in the upper parts of the cochlea.
The researchers have now studied the details of this process, almost down to cell level. To do so, they used synchrotron X-rays, an advanced and powerful form of tomographic imaging. Since the radiation is too strong to be used on living human beings, donated ears from deceased people were investigated instead. This research has made it possible to work out the locations of the various frequencies in the cochlear nerve, and enabled the creation of a three-dimensional tonotopic frequency map.
“This kind of map is comparable to a piano, with the keys being analogous to all the similarly coded frequencies. Unlike the piano, which has 88 keys, we have about 3,400 internal auditory hair cells, all of which encode distinct frequencies. The hair cells are attached to a 34-millimetre-long basilar membrane, and are also tuned by 12,000 outer hair cells so that we can hear every volume level. This information is mediated to the brain via 30 000 precisely tuned fibres in our hearing nerve,” Helge Rask-Andersen explains.
Human ear canals and nerves are not entirely uniform in appearance. The researchers therefore think the new knowledge may prove immensely important for people who, owing to grave hearing impairments, have cochlear implants (CIs) inserted. A CI is a hearing aid where one component is placed in the cochlea to provide direct electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve, while another part is attached to the outside of the skull. Showing exactly what the patient’s cochlea looks like enables the technology to be individualised better and each area stimulated with the right frequency.
###
The study is a collaboration between Uppsala University, Canadian researchers at Western University and University of Saskatchewan, and the company Canadian Light Source Inc.
Hao Li et al., Three?dimensional tonotopic mapping of the human cochlea based on synchrotron radiation phase?contrast imaging, Scientific Reports. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83225-w
Media Contact
Helge Rask-Andersen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.