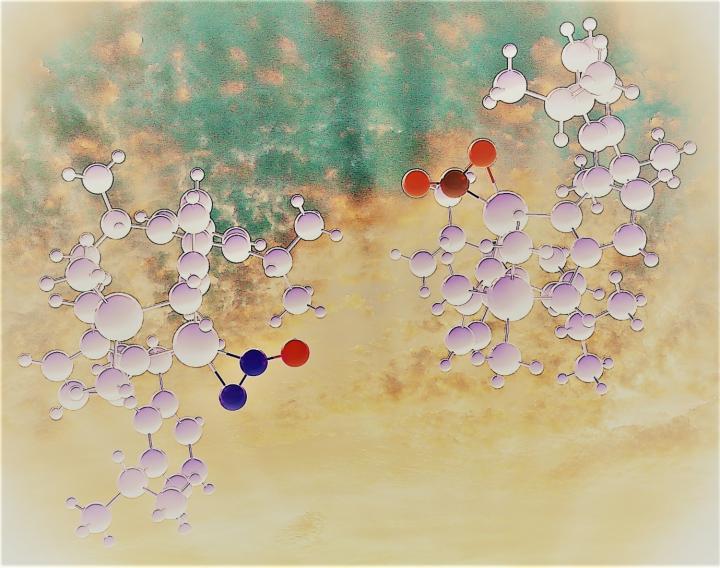
Credit: Monika Stolar and Chris Gendy
Like its chemical relative carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide (N2O) is an important greenhouse gas and the dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st Century. Consequently, strategies for limiting its emissions and its catalytic decomposition with metals are being developed. A recent study indicates that nitrous oxide can bind to metals similarly to carbon dioxide, which helps to design new complexes with even stronger bonding. This could allow the use of nitrous oxide in synthetic chemistry or help to degrade it to substances harmless to the atmosphere. The results were reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition as a Very Important Paper on February 17th 2021.
A comprehensive analysis of the global N2O budget has shown that its emissions have been increasing for the past four decades, with agricultural activities responsible for the growth. Even though N2O is present in the atmosphere at a concentration 1000 times less than CO2, it is approximately 300 times more potent as a greenhouse gas.
In nature, N2O is converted by enzymes into N2 and H2O. The process can be mimicked in a laboratory setting using catalytic metal complexes. Surprisingly, well-defined complexes of N2O with transition metals are exceedingly rare, even though CO2 has rich and well-documented coordination chemistry. The vastly dissimilar behaviour of these two related small molecules has been attributed to the poor ligand characteristics of N2O in comparison to CO2, but the origins and details of this justification are difficult to track.
“The more information we tried to find on the topic, the closer we headed to circular reasoning,” says Dr. Heikki M. Tuononen from the University of Jyväskylä, Finland. “In many cases, some property of N2O was highlighted, but they are almost all characteristic to CO2 as well”, he continues.
“This puzzle was one of the reasons why, during Dr. Tuononen’s visit to Calgary as a Killam Scholar, our research teams decided to join forces and synthesize analogous metal complexes of N2O and CO2, and study the metal-ligand interaction in detail”, tells Dr. Roland Roesler from the University of Calgary, Canada.
A rare metal complex of N2O stable even at room temperature
The results of the two-year investigation showed that, contrary to the general view, the metal binding ability of N2O is equally good or even better than that of CO2.
“It appears that the oxidizing character of N2O is mostly, if not entirely, responsible for the scarcity of metal complexes employing this ligand”, says Dr. Tuononen.
“Once we had the right metal partner for N2O, their binding was strong enough that a rare side-on bound complex could be isolated and characterized even at room temperature”, continues Dr. Chris Gendy, a former Ph.D. student at University of Calgary who was partially responsible of the synthetic work.
In addition to showing that N2O has better intrinsic ability to bind to metals than heretofore recognized, the work of the two research teams allows the rational design of N2O complexes that are even more stable than the ones characterized thus far. This could, in turn, open new avenues for using N2O in synthetic chemistry.
“N2O is in many ways a great oxidant. It is thermodynamically strong, relatively cheap, and gives N2 as the only side product”, explains Dr. Tuononen.
“It would certainly be great to see more widespread use of N2O as an oxidant in metal-catalysed reactions. At the same time, we should not forget the role it plays in the atmosphere”, adds Dr. Roesler.
“Nature has found elegant enzymatic pathways to convert N2O into products that are harmless to the atmosphere. We should aim for the same with our manmade emissions using novel catalysts”, the research teams conclude.
###
The paper “Side?on Coordination in Isostructural Nitrous Oxide and Carbon Dioxide Complexes of Nickel” by Braulio Michele Puerta Lombardi, Chris Gendy, Benjamin S. Gelfand, Guy M. Bernard, Roderick E. Wasylishen, Heikki M. Tuononen and Roland Roesler was published online as a Very Important Paper in Angewandte Chemie International Edition on February 17th 2021.
Link to publication:
https:/
Research resources for the project have been provided by the Universities of Calgary, Jyväskylä, and Alberta, as well as Canada Foundation for Innovation and Finnish Grid and Cloud Infrastructure. The project also received funding from the European Research Council under the EU’s Horizon 2020 programme (Grant #772510 to H.M.T.) as well as from the NSERC of Canada in the form of Discovery Grants (#2019-07195 to R.R. and #2019-06816 to R.E.W).
More information:
Heikki M. Tuononen,
tel. +358-40-805-3713,
[email protected]
Roland Roesler,
tel. +1-403-220-5366,
[email protected]
Media Contact
Dr. Heikki M. Tuononen
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




