Credit: by Gan Huang, Kai Wang and Christos N. Markides.
Solar energy is one of the most abundant renewable energy sources, and effective solar technologies have great potential to alleviate the grand challenges of rising global energy demands, while reducing associated emissions. Solar energy is capable of satisfying the electrical and thermal-energy needs of diverse end-users by means of photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal (ST) technologies, respectively. Recently, hybrid photovoltaic-thermal (PVT) concepts have been proposed that synergistically combine the benefits of PV and ST technologies, and are capable of generating both electricity and useful heat simultaneously from the same area and component.
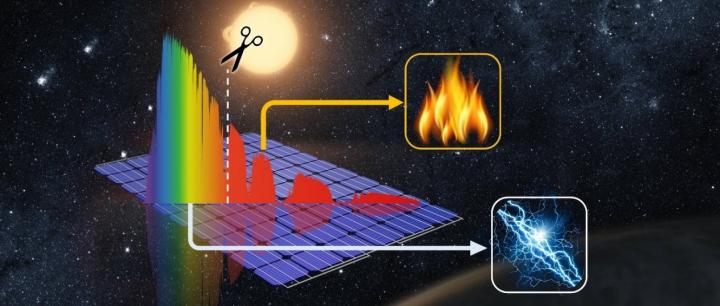
Spectral splitting is an emerging approach for designing high-performance PVT solar collectors, which employ advanced designs with optical filters that direct different parts of the solar spectrum either to the PV cells for electricity generation or to a thermal absorber for heat generation. Nevertheless, the ultimate efficiency limits of spectral-splitting PVT (SSPVT) collectors depending on the application and end-user demands, along with the optimal collector designs, PV cell and optical filter materials that can enable us to approach these limits have remained unclear, with a lack of consensus in the field, motivating a closer examination of these aspects of SSPVT technology.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, Christos N. Markides and Gan Huang from Imperial College London in the UK, in collaboration with Kai Wang from Zhejiang University in China, report a comprehensive framework for predicting the performance of such collectors, which is then used to identify their efficiency limits, and to provide detailed guidance for selecting optimal PV materials and optimal spectral-splitting filters capable of delivering a combined thermal and electrical performance that approaches the efficiency limits of this technology.
“We found that the relative value of thermal energy to that of electricity has a significant influence on the total effective efficiency limits, the optimal PV cell material and the optimal spectral-splitting filter of SSPVT collectors.”
“CIGS solar cells are considered particularly promising for SSPVT collector applications owing to their adjustable bandgap energy. The optimal lower- and upper-bounds of the spectral-splitting filter depend strongly on the PV material” they added.
“Detailed maps in our research can assist designers in selecting appropriate solar-cell materials and spectral-splitting optical filters, depending on the conditions and application, in order to achieve optimal overall performance accounting for both energy vectors (electricity and heat) generated by these systems.” the scientists stated.
###
Media Contact
Gan Huang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




