Light provides freedom to control each layer and improves precision and speed
Credit: Northwestern University
The speed of light has come to 3D printing. Northwestern University engineers have developed a new method that uses light to improve 3D printing speed and precision while also, in combination with a high-precision robot arm, providing the freedom to move, rotate or dilate each layer as the structure is being built.
Most conventional 3D printing processes rely on replicating a digital design model that is sliced into layers with the layers printed and assembled upwards like a cake. The Northwestern method introduces the ability to manipulate the original design layer by layer and pivot the printing direction without recreating the model. This “on-the-fly” feature enables the printing of more complicated structures and significantly improves manufacturing flexibility.
“The 3D printing process is no longer a way to merely make a replica of the designed model,” said Cheng Sun, associate professor of mechanical engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering. “Now we have a dynamic process that uses light to assemble all the layers but with a high degree of freedom to move each layer along the way.”
Sun led the research, which lies at the intersection of two of his main areas of focus: nanofabrication and optics. The study was published today (Feb. 3) by the journal Advanced Materials.
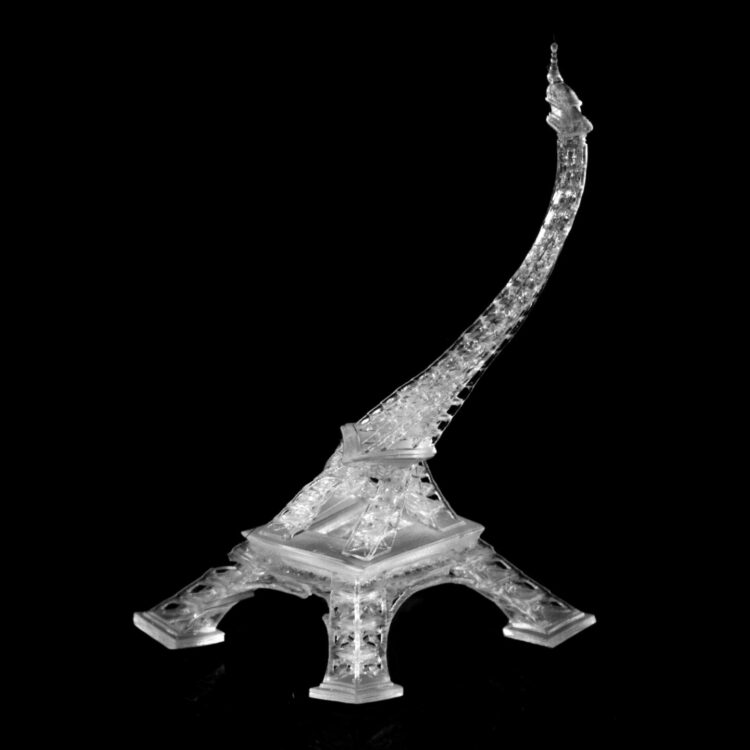
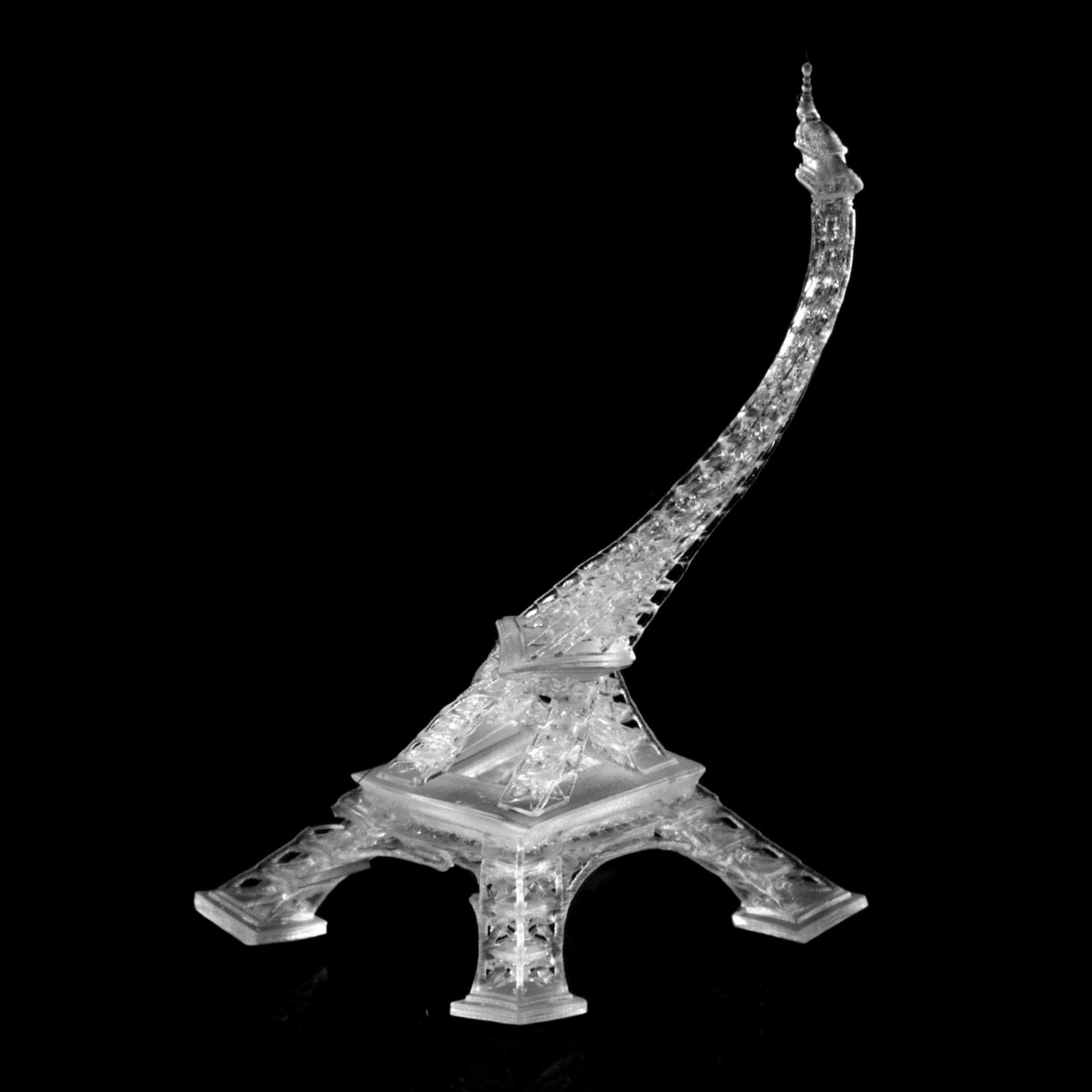
In the paper, the researchers demonstrate several applications, including 3D printing a customized vascular stent and printing a soft pneumatic gripper made of two different materials, one hard and one soft. A double helix and a tiny Eiffel Tower are two other printed examples in the study.
The Northwestern process uses a robotic arm and a liquid photopolymer that is activated by light. Sophisticated 3D structures are pulled out from a bath of liquid resin by a high-precision robot with enhanced geometric complexity, efficiency and quality compared to the traditional printing process. The arm is used to change the printing direction dynamically.
“We are using light to do the manufacturing,” Sun said. “Shining light on the liquid polymer causes it to crosslink, or polymerize, converting the liquid to a solid. This contributes to the speed and precision of our 3D printing process — two major challenges that conventional 3D printing is facing.”
The continuous printing process can print 4,000 layers in approximately two minutes.
“This is a very fast process, and there is no interruption between layers,” Sun said. “We hope the manufacturing industry will find benefit in it. The general printing method is compatible with a wide range of materials.”
Looking to the future, Sun said this printing process could be applied to other additive as well as traditional subtractive manufacturing processes, providing a bridge toward a truly hybrid process.
###
The title of the paper is “Conformal Geometry and Multimaterial Additive Manufacturing through Freeform Transformation of Building Layers.”
Media Contact
Megan Fellman
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.