These high-entropy alloys could lead to better technologies in transportation, energy and denfense
Credit: University of California San Diego
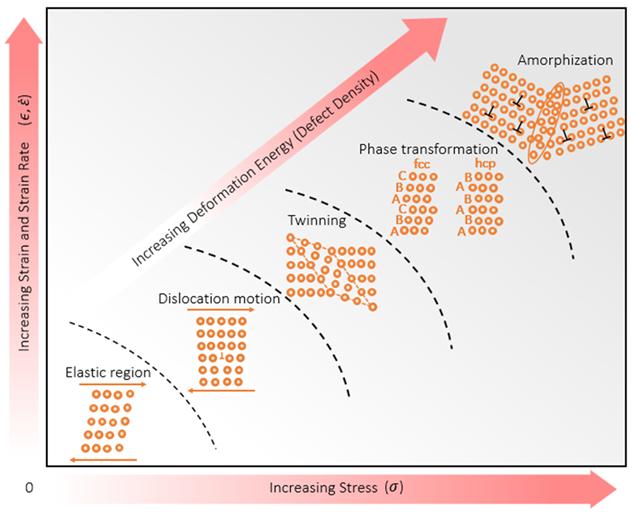
An international team of researchers produced islands of amorphous, non-crystalline material inside a class of new metal alloys known as high-entropy alloys.
This discovery opens the door to applications in everything from landing gears, to pipelines, to automobiles. The new materials could make these lighter, safer, and more energy efficient.
The team, which includes researchers from the University of California San Diego and Berkeley, as well as Carnegie Mellon University and University of Oxford, details their findings in the Jan. 29 issue of Science Advances.
“These present a bright potential for increased strength and toughness since metallic glasses (amorphous metals) have a strength that is vastly superior to that of crystalline metals and alloys,” said Marc Meyers, a professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at UC San Diego, and the paper’ s corresponding author.
Using transmission electron microscopy, which can identify the arrangement of atoms, the researchers concluded that this amorphization is triggered by extreme deformation at high velocities. It is a new deformation mechanism that can increase the strength and toughness of these high entropy alloys even further.
The research is based on seminal work by Brian Cantor at the University of Oxford, and Jien-Wei Yeh at National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan. In 2004, both researchers led teams that reported the discovery of high-entropy alloys. This triggered a global search for new materials in the same class, driven by numerous potential applications in the transportation, energy, and defense industries.
“Significant new developments and discoveries in metal alloys are quite rare,” Meyers said.
###
Amorphization in extreme deformation of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
Shiteng Zhao and Robert O. Ritchie, University of California Berkeley; Zezhou Li, Wen Yang and Marc A. Meyers, University of California San Diego; Chaoyi Zhu, Carnegie Mellon University; Zhouran Zhang, David E. J. Armstrong and Patrick S. Grant, University of Oxford.
Media Contact
Ioana Patringenaru
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




