Therapeutic efficacy prediction using initial distribution images of stem cells that differentiate to endothelial cells; applied to research in the field of stem cell treatments for blood vessel regeneration
Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST)
In recent years, the number of high-risk groups for ischemic diseases such as critical limb ischemia where tissues of toe may decay is increasing due to increase in the number of people with obesity, diabetes, and hypertension which are triggered by changes in dietary habits, and consumption of smoking and alcohol. A number of studies are actively conducted on endothelial progenitor cells (hEPCs), which are stem cells that contribute to the blood vessel regeneration in the ischemic tissues, to treat such ischemia diseases.
Vascular hEPCs migrate to regions requiring angiogenesis, such as ischemic regions, and then differentiate into endothelial cells of blood vessels or release growth factors that help formation of blood vessels to induce regeneration of the damaged blood vessels. Hence, these cells can be developed into stem cell therapy for diseases related to blood vessels including ischemic diseases.
However, when the hEPCs with outstanding blood vessel regeneration capability are used as stem cell therapy in ischemic diseases, the therapeutic treatment efficacy may differ depending on various variables such as survival of the transplanted cells and migration to the treatment region. Accordingly, treatments for ischemic diseases are remaining in the clinical stage without being commercialized due to the limitations in accurately observing and predicting the therapeutic efficacy.
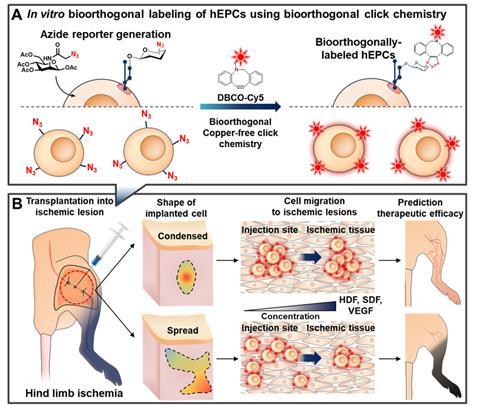
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) recently announced that the collaborative research team led by Dr. Kwangmeyung Kim from Center for Theragnosis and Sung-Hwan Moon from Stem Cell Research Institute, T&R Biofab Co. Ltd developed a method that can predict the therapeutic efficacy based on the distribution of the initial transplantation of hEPCs by tracking the initial distribution and migration of the transplanted cells using fluorescence romographic images.
The KIST research team first enabled observing fluorescence signals through fluorescence molecular tomography by binding fluorescent dyes to the surface of hEPCs. Subsequently, the team transplanted the cells into the hind limb of mouse with severe limb ischemia and tracked them through images for 28 days to evaluate the cell movement in the body; then, tracked and observed the regeneration process of the blood flow through laser scanning microscope(Laser Doppler imaging). As a result, it was revealed that the hEPCs migrate to the damaged tissues where the ischemic disease is found.
Additionally, the shapes of cell clusters were observed to be injected in two different shapes as a result of analyzing the images of hEPCs during the initial transplantation of the cell therapy treatment. The two shapes were condensed round shape and spread shape. When the therapeutic efficacy was observed by classifying the experimental groups into these two shapes, it was found that the initial condensed ’round shape’ cells migrated better and showed superior therapeutic efficacy in the experimental groups. Based on these findings, the research team predicted that the treatment efficacy will be superior when the treatment cells are formed into a condensed ’round shape’ during the initial treatment.
“Our developed technology, which can quickly and accurately monitor the initial transplantation forms and changes of stem cell therapy, will enable predicting the efficacy of the transplanted hEPCs in the early stages of ischemic disease treatments, and we expect it to be used in the development of stem cell therapy treatments for ischemic diseases in the future,” said Dr. Kwangmeyung Kim at KIST, who led the research.
###
This study was carried out with a grant from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), as part of the Institutional R&D Program of KIST and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea. The findings were reported in the latest edition of the international journal, ‘Biomaterials‘ (IF: 10.317, Top 1.316% in the field of JCR).
Media Contact
Do-Hyun Kim
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




