Credit: Courtesy of Dr. Wei Lü, Van Andel Institute
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Nov. 4, 2020) — For the first time, scientists have visualized a new class of molecular gates that maintain pH balance within brain cells, a critical function that keeps cells alive and helps prevent stroke and other brain injuries.
These gates, called proton-activated chloride channels (PAC), nest within cell membranes and regulate the passage of small molecules called chloride ions into and out of cells. This allows cells to sense and respond to their environment.
“Proton-activated chloride channels have only recently been described but they are critical for cell survival, particularly in the brain,” said Wei Lü, Ph.D., a Van Andel Institute assistant professor and co-corresponding author of the study, which was published today in Nature. “Our new images, coupled with our findings into how these channels work, provide much-needed molecular blueprints that will help answer long-standing questions in the field and provide new insights into how these channels may be therapeutically targeted in disease.”
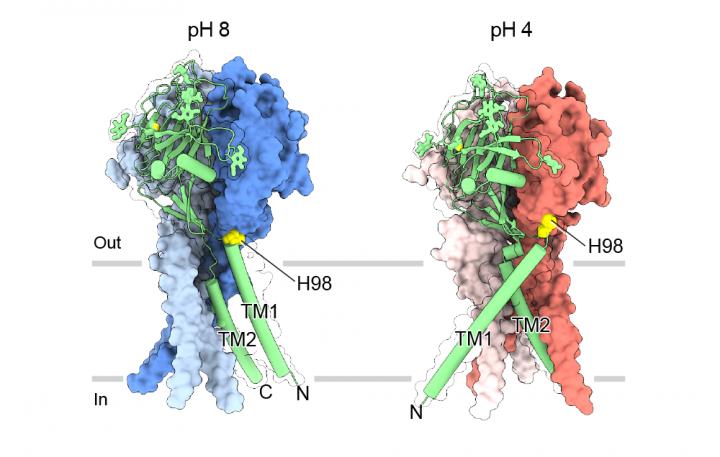
The images reveal a wedding bouquet-like structure, with parts that change configuration in response to environmental pH. When pH shifts from alkaline to acidic, a key pH sensor moves from its “resting” location and is inserted in an “acidic pocket,” which signals that the gate allowing ions in and out of the cell should be open. This specific mechanism has never before been described.
This study is a collaboration between the Lü Lab at Van Andel Institute and a group led by Zhaozhu Qiu, Ph.D., an assistant professor at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and co-corresponding author of the paper. The Johns Hopkins team first reported the discovery of PAC in Science last year.
Solving PAC structures are another important, early step toward an understanding that may one day impact human health.
###
Other authors include co-first author Zheng Ruan, Ph.D., of VAI, and co-first author James Osei-Owusu, of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; and VAI Assistant Professor Juan Du, Ph.D. PAC was visualized through use of cryo-EM at the David Van Andel Advanced Microscopy Suite at Van Andel Institute.
Research reported in this publication was supported by Van Andel Institute; McKnight Scholar Awards in Neuroscience (Du, Qiu), Klingenstein-Simons Scholar Awards (Du, Qiu); Sloan Research Fellowships (Du, Qiu); the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under award no. R35GM124824 (Qiu); the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke of the National Institutes of Health under award no. R01NS118014 (Qiu), R01NS112363 (Lü) and R01NS111031 (Du); the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award no. R56HL144929 (Lü); a Pew Scholar in Biomedical Sciences award (Du); and the American Heart Association under award no. 20POST35120556 (Ruan) and 18PRE34060025 (Osei-Owusu). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the granting organizations.
ABOUT VAN ANDEL INSTITUTE
Van Andel Institute (VAI) is committed to improving the health and enhancing the lives of current and future generations through cutting edge biomedical research and innovative educational offerings. Established in Grand Rapids, Michigan, in 1996 by the Van Andel family, VAI is now home to more than 400 scientists, educators and support staff, who work with a growing number of national and international collaborators to foster discovery. The Institute’s scientists study the origins of cancer, Parkinson’s and other diseases and translate their findings into breakthrough prevention and treatment strategies. Our educators develop inquiry-based approaches for K-12 education to help students and teachers prepare the next generation of problem-solvers, while our Graduate School offers a rigorous, research-intensive Ph.D. program in molecular and cellular biology. Learn more at vai.org.
Media Contact
Beth Hinshaw Hall
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




