Credit: Simon Scarpetta
In 2017, while browsing the fossil collections of Yale’s Peabody Museum of Natural History, University of Texas at Austin graduate student Simon Scarpetta came across a small lizard skull, just under an inch long.
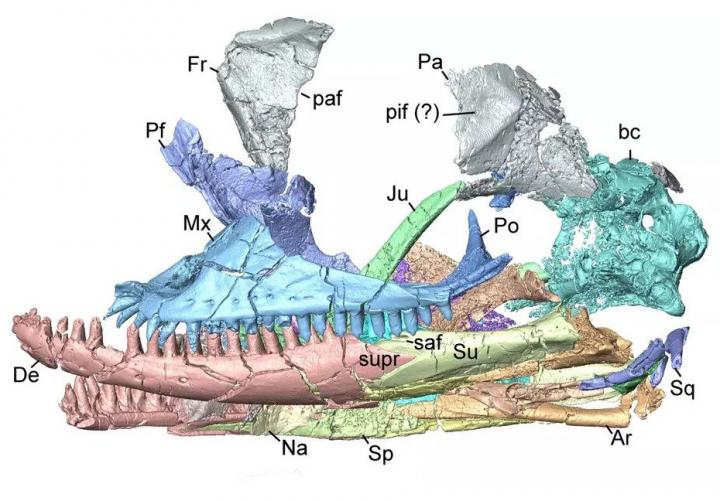
The skull was beautifully preserved, with a mouth full of sharp teeth – including some with a distinctive curve.
Much to Scarpetta’s surprise, no one had studied it. Since being discovered in 1971 on a museum fossil hunting trip to Wyoming, the 52 million-year-old skull had sat in the specimen drawer.
“Lizards are small and prone to breaking apart, so you mostly get these individual, isolated fragmented bones,” said Scarpetta, who is studying paleontology at the UT Jackson School of Geosciences. “Anytime you find a skull, especially when you’re trying to figure out how things are related to each other, it’s always an exciting find.”
Scarpetta decided to bring the skull back to the Jackson School for a closer look. And on September 2020, the journal Scientific Reports published a study authored by Scarpetta describing the lizard as a new species, which he named Kopidosaurus perplexus.
The first part of the name references the lizard’s distinct teeth; a “kopis” is a curved blade used in ancient Greece. But the second part is a nod to the “perplexing” matter of just where the extinct lizard should be placed on the tree of life. According to an analysis conducted by Scarpetta, the evidence points to a number of plausible spots.
The spots can be divided into two groups of lizards, representing two general hypotheses of where the new species belongs. But adding to the uncertainty is that how those two groups relate to one another can shift depending on the particular evolutionary tree that’s examined. Scarpetta examined three of these trees – each one built by other researchers studying the evolutionary connections of different reptile groups using DNA – and suggests that there could be a forest of possibilities where the ancient lizard could fit.
The case of where exactly to put the perplexing lizard highlights an important lesson for paleontologists: just because a specimen fits in one place doesn’t mean that it won’t fit equally well into another.
“The hypothesis that you have about how different lizards are related to each other is going to influence what you think this one is,” Scarpetta said.
Paleontologists use anatomical details present in bones to discern the evolutionary relationships of long-dead animals. To get a close look at the lizard skull, Scarpetta created a digital scan of it in the Jackson School’s High-Resolution X-Ray CT Lab. However, while certain details helped identify the lizard as a new species, other details overlapped with features from a number of different evolutionary groups.
All of these groups belonged to a larger category known as Iguania, which includes a number of diverse species, including chameleons, anoles and iguanas. To get a better idea of where the new species might fit into the larger Iguania tree, Scarpetta compared the skull data to evolutionary trees for Iguania that were compiled by other researchers based on DNA evidence from living reptiles.
On each tree, the fossil fit equally well into two general spots. What’s more, the lizard groupings in each spot varied from tree to tree. If Scarpetta had just stopped at one spot or one tree, he would have missed alternative explanations that appear just as plausible as the others.
Scarpetta said that Kopidosaurus perplexus is far from the only fossil that could easily fit onto multiple branches on the tree of life. Paleontologist Joshua Lively, a curator at the Utah State University Eastern Prehistoric Museum, agrees and said that this study epitomizes why embracing uncertainty can lead to better, more accurate science.
“Something that I think the broader scientific community should pull from this is that you have to be realistic about your data and acknowledge what we can actually pull from our results and conclude and where there are still uncertainties,” Lively said. “Simon’s approach is the high bar, taking the high road. It’s acknowledging what we don’t know and really embracing that.”
###
The research was funded by the Jackson School of Geosciences and the Geological Society of America.
Media Contact
Monica Kortsha
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




