Credit: © Bettina Heider et al. Nature Climate Change
Climate change poses a threat to the world’s subsistence crops. Heatwaves, which are likely to intensify according to climate evolution predictions, are generating levels of heat stress that are damaging to agricultural production. Identifying resistant crop varieties is therefore crucial to ensuring people’s food security and farmers’ resilience. To date, many studies have been conducted on varietal improvement, which involves developing and selecting plants with the required characteristics. Few, however, have examined intraspecific diversity, which is defined as the degree of genetic variety that exists within the same species.
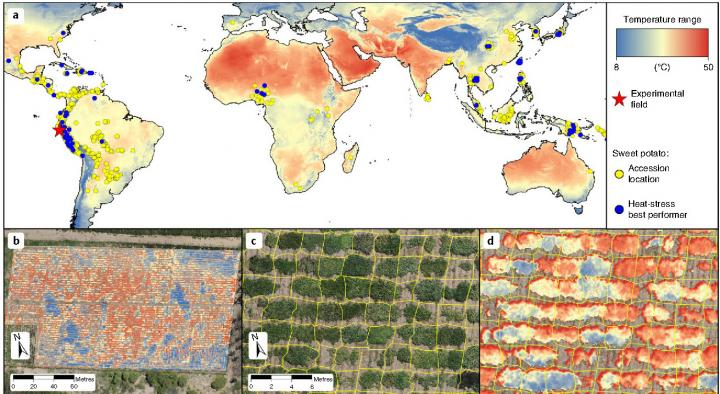
For the present study, the international team focused on the sweetpotato – the fifth most produced crop in the world, after corn, wheat, rice, and cassava. This tuber is grown for its hardiness and tolerance to climatic shocks, and has great potential to help achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations as part of the Horizon 2030 Agenda: it is grown in areas prone to erosion to protect agricultural land (SDGs 12 and 15); it has a high nutritional value, as well as higher content than most staple foods in vitamins A and C, calcium, iron, dietary fibre, and protein (SDGs 2 and 3); its flexible planting and harvesting schedules mean it is less labour-intensive to grow and thus is particularly adaptable to human migration (SDGs 10 and 16).
Traditional local varieties perform well under heat stress
As part of CGIAR’s research program on roots, tubers and bananas (RTB), the researchers assessed the heat-stress tolerance of 1,973 different varieties of sweetpotato from the CIP’s sweet-potato ‘genebank’. The collection of cultivars from 50 different countries comprised modern and traditional varieties, as well as breeding lines, developed in vitro and then planted in fields irrigated under controlled conditions on a 2.5 ha test site in the coastal desert region of north Peru. Analysis of the roots and foliage data allowed the effect of repeated exposure to extreme temperatures – greater than 35°C – on the plants’ performance to be measured.
Result: “132 cultivars, of which 65.9% were traditional local varieties, demonstrated good heat tolerance. These are therefore promising candidates for selection as high-yield, heat-tolerant varieties,” explains Bettina Heider, a researcher with CIP and lead author of the study.
“This mass screening, carried out on an unprecedented geographical scale (America, Africa, Asia), proved crucial to identifying the heat-stress tolerance characteristics of the sweetpotato, for the purpose of a deeper molecular characterization of specific genes,” explains Olivier Dangles, an ecologist at IRD and co-author of the study.
“Intraspecific diversity – the result of hundreds of years of co-evolution between farmers and their crops – is proving critical in the face of climate change,” he continues. “It emphasizes the role of agrobiodiversity in the resilience of tropical agricultural systems.”
Farmers will need help to adapt
“Our results also suggest that the temperature of the canopy and the level of carotenoids could be the appropriate markers for selecting heat-stress tolerant lines,” adds Emile Faye, researcher in spatial agroecology at CIRAD. “However, participatory experiments need to be conducted in different contexts, to test the efficacy and economic viability of the varieties identified.”
Intraspecific diversity offers more options to farmers, therefore, for managing climate risks and increasing the resilience of their farming systems. The study authors recommend that this knowledge be shared with farmers, so that they adopt high-yield varieties that also offer higher nutritional value.
###
Media Contact
Cristelle Duos (IRD press officer)
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




